Exam 4 H+E
1/536
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
537 Terms
What do kidneys do, generally
excretion and removal of metabolic waste and foreign substances
maintain fluid volume, pH, blood pressure, electrolytes
secrete hormones
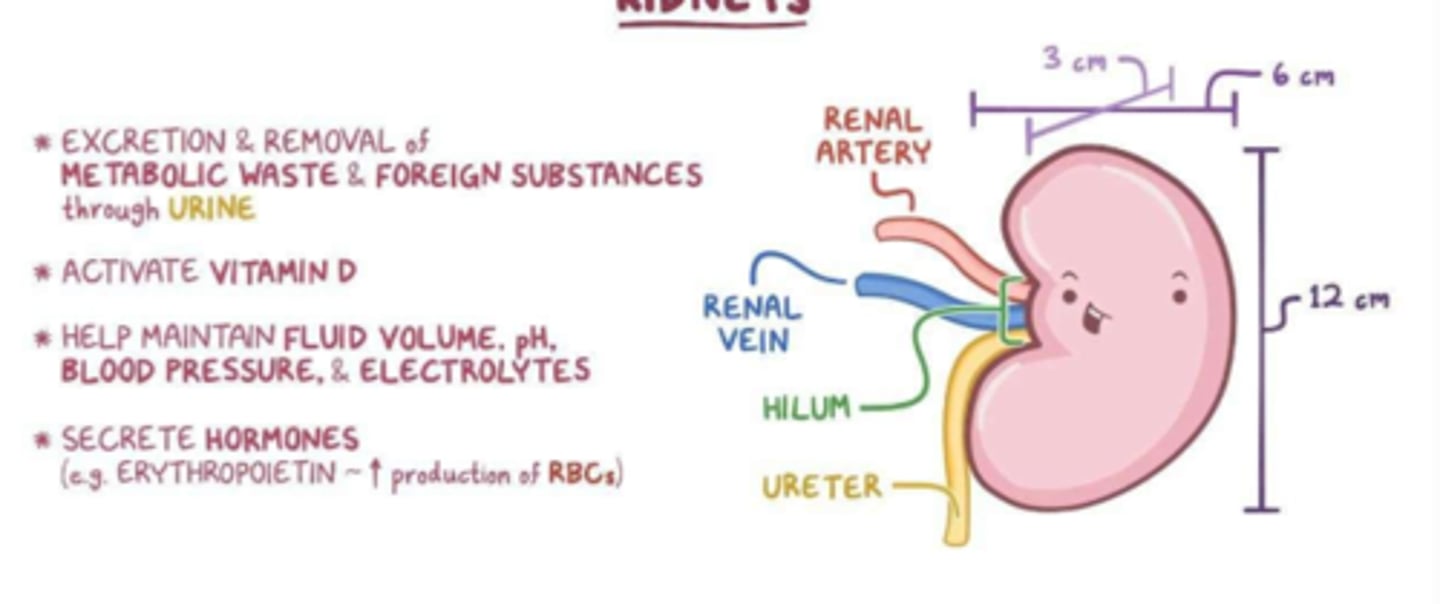
which vitamin do the kidneys activate
vitamin D
what blood-related hormone do the kidneys secrete
erythropoietin - production of RBCs in the bone marrow
two parts the urogenital system is divided into
urinary system and genital system
What comes from the intermediate mesoderm 3
gametes, adrenal cortex, urogenital stuff
names of the 3 pairs of kidneys
pronephros, mesonephros, and metanephros (what we still have)
what does the ductus deferens come from
mesonephric duct (AKA wolffian)
what does the urogenital system derive from
intermediate mesoderm
(and mesodermal coelomic epithelium)
what is the embryonic structure that the urinary and genital systems develop from
urogenital ridge
the medial part of the urogenital ridge turns into ______________, specifically the ___________ cords
urinary system, neophrogenic cords
what are the two parts of the urogenital ridge
nephrogenic cords
gonadal ridge
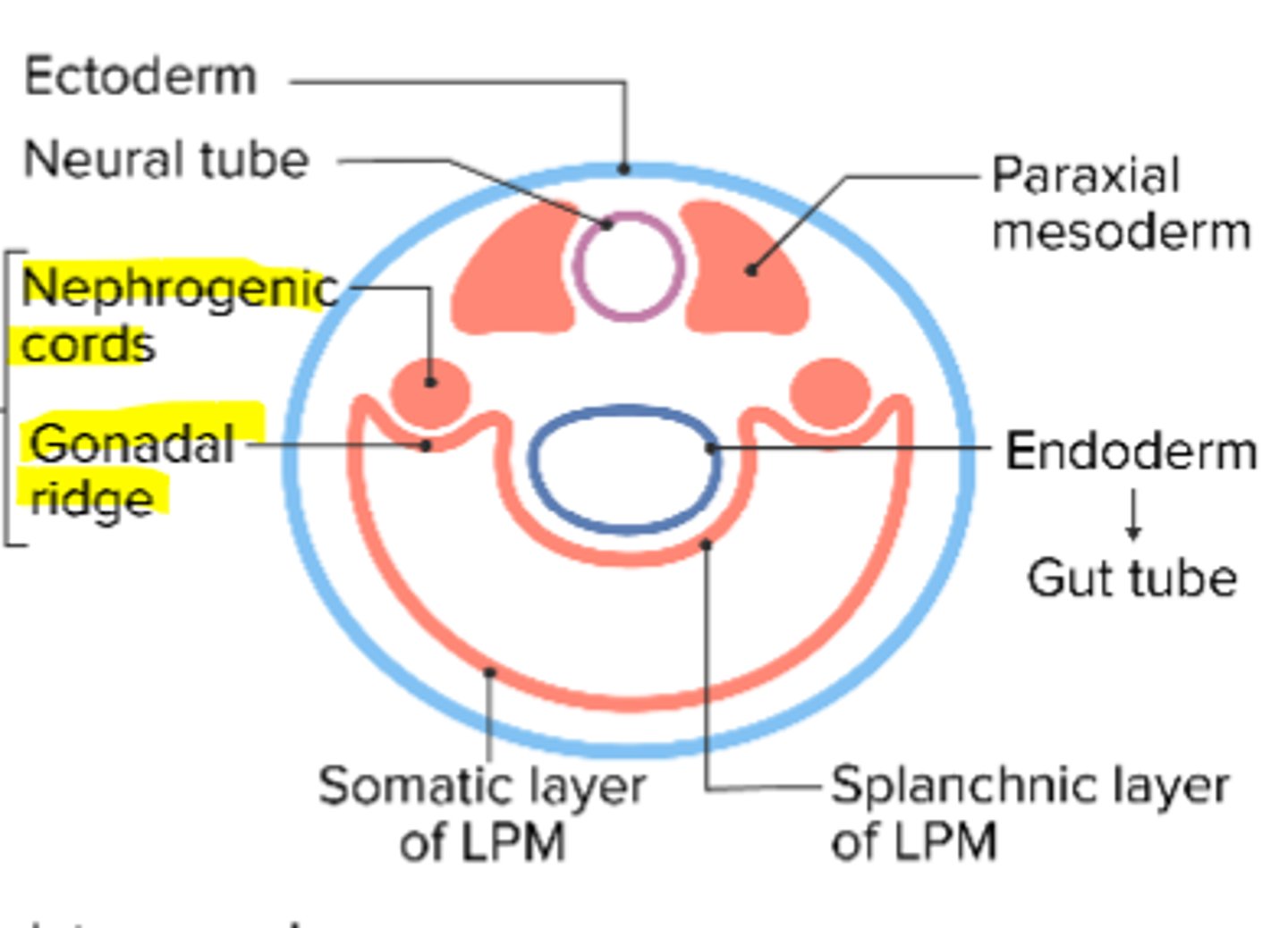
what does the nephrogenic cord turn into
kidneys, ureter, make ducts
name for mammalian kidney formation
nephrogenesis
how do the three primordial kidneys arise in the embryo
in an anterior-posterior wave of cellular differentiation in the nephrogenic cord, (part of the urogenital ridge)
as the three primordial sets of kidneys arise, their excretory ducts are localized (parallel/perpendicular) to the nephrogenic cord
parallel
what does the gonadal ridge turn into
ovary/testis and female/male genital tract
in (mammals/fish) the pronephros is significant. In (mammals/fish), the pronephros is rudimentary and short lived
fish, mammals
in (mammals/amphibians) the mesonephros is fully operational. In (mammals/amphibians) the mesonephros is transitory.
amphibians (and other lower vertebrates), mammals
which kidney is permanent in mammals
metanephros
the nephrogenic cord/mesonephros forms (anterior to posterior, or posterior to anterior)
anterior to posterior
order of kidneys forming
pronephros, mesonephros, metanephros
what happens to the pronephros when the mesonephros is developing
it starts to degenerate
what happens when the metanephros is forming
the mesonephros begins degenerating
the mesonephros starts degenerating (anterior->posterior or posterior->anterior)
anterior->posterior
structure of the pronephros
paired organ, with a giant nephron that processes blood filtrate produced from the glomeruli
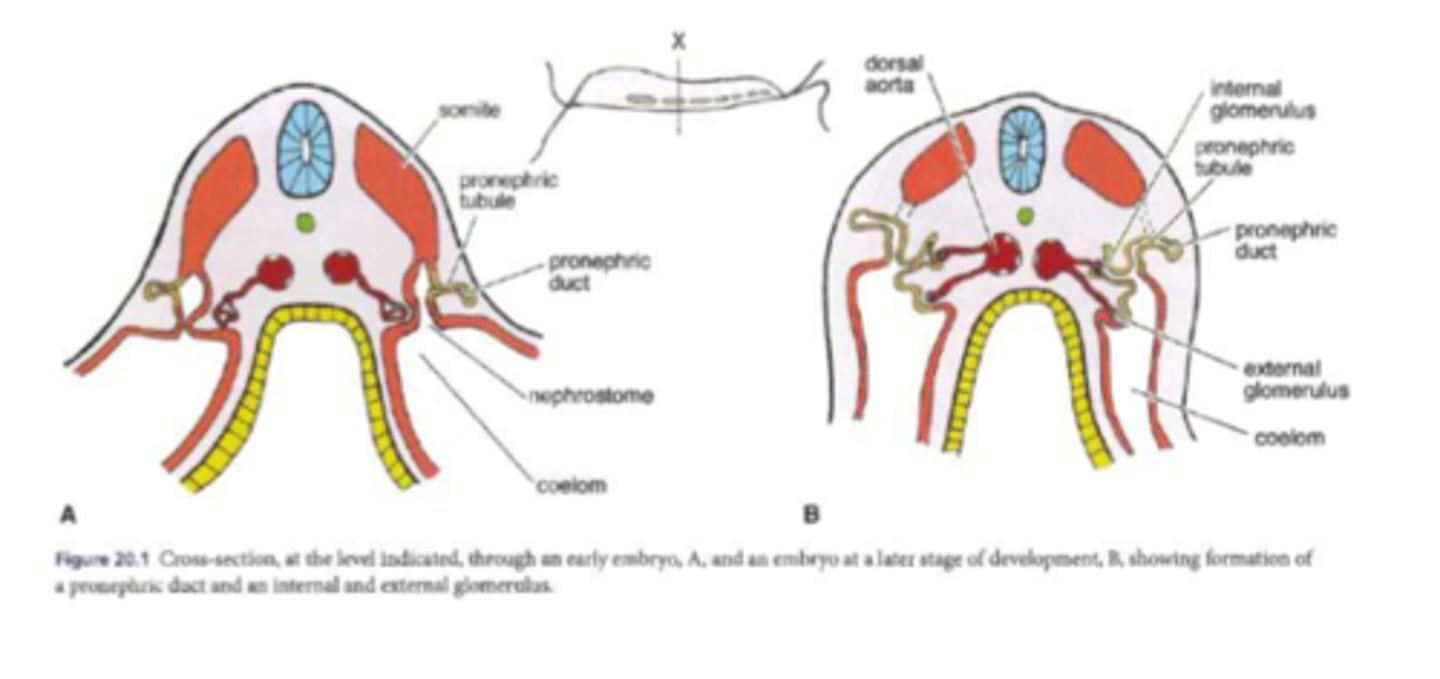
where does the pronephros deposit the filtrate
the coelom of the embryo
mesonephros (and its duct) location
upper thoracic to upper lumbar segments of the embryo
in domestic animal embryos, how many mesonephric tubules appear in the levels of somites 9-26
70-80 (really big kidney, running along length of embryo)
what is on either side of a mesonephric tubule
blood vessel on one side, posterior end of pronephric duct on other
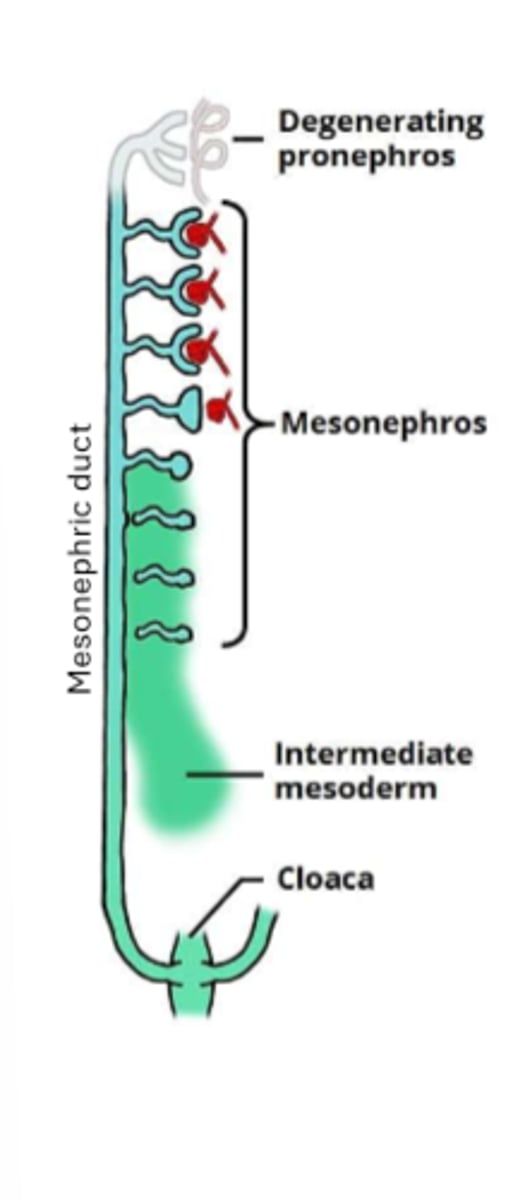
the mesonephric duct connects: (3 things)
primitive kidney/mesonephros, cloaca and allantois
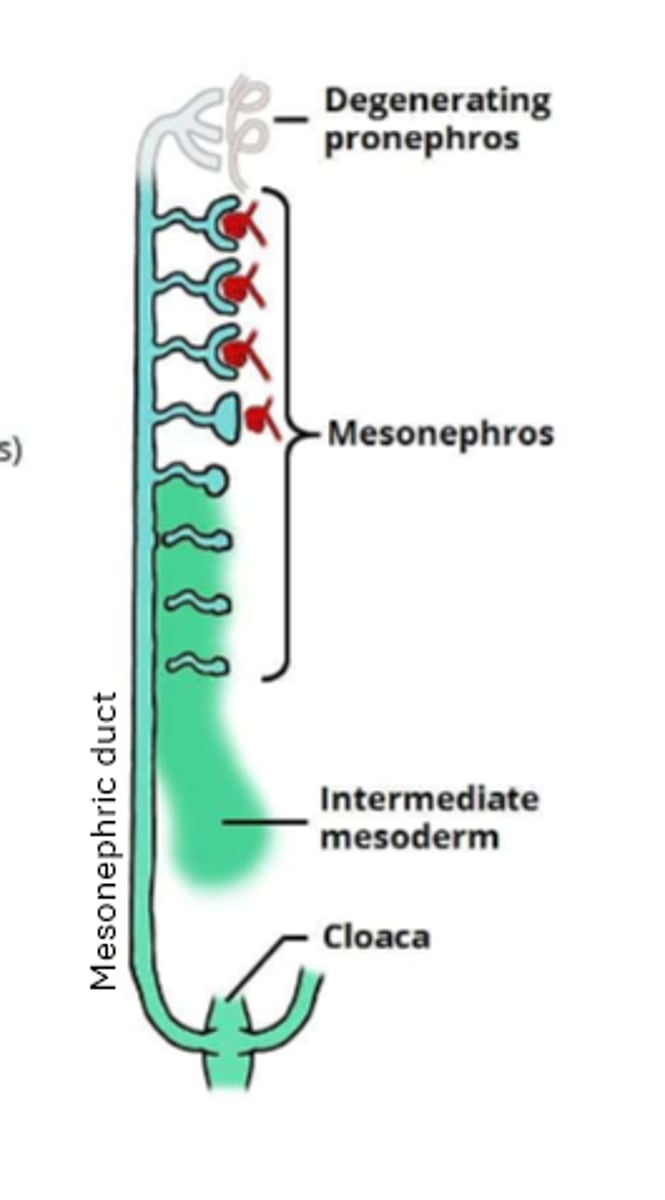
location of the metanephric duct in the embryo
pretty caudal
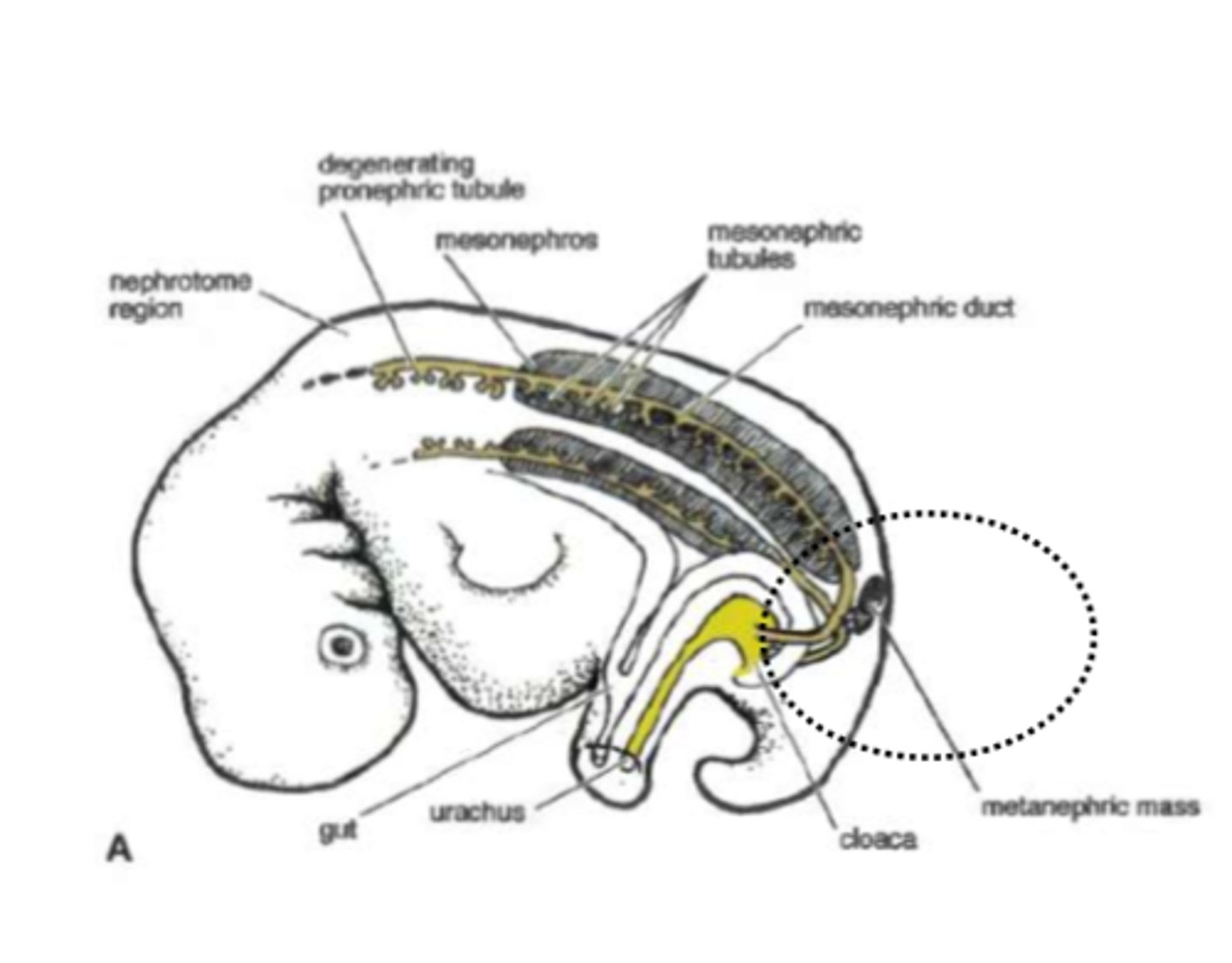
wolffian duct =
mesonephric duct
the metanephros develops from the induction of the ___________________ ______________ by the ureteric bud
metanephric mesenchyme
what does the ureteric bud come off of
wolffian duct (mesonephric duct)
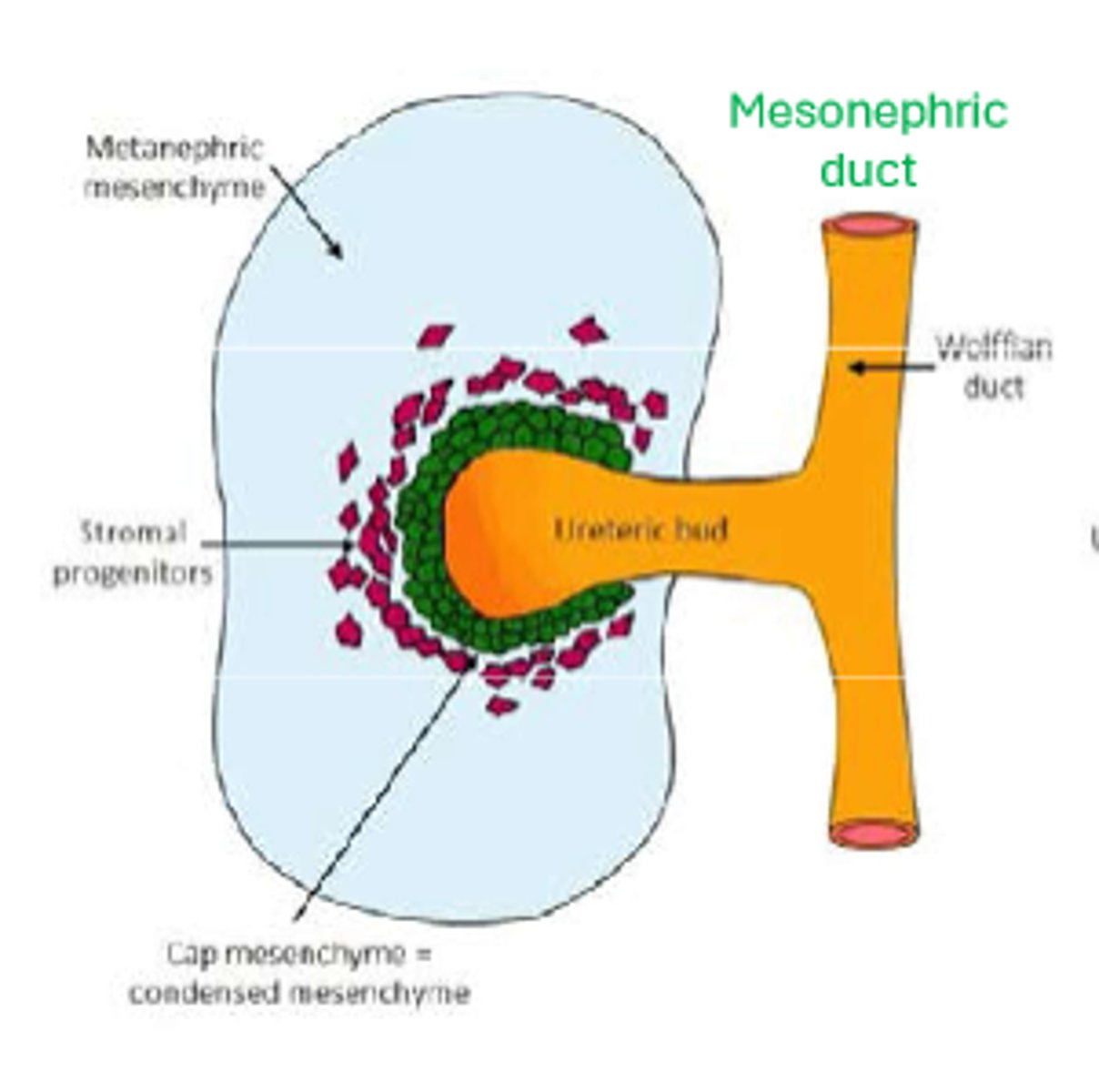
as the ureteric bud keeps branching, what does the metanephric mesenchyme make around the tips of the branching structure?
renal vesicles (second pic)
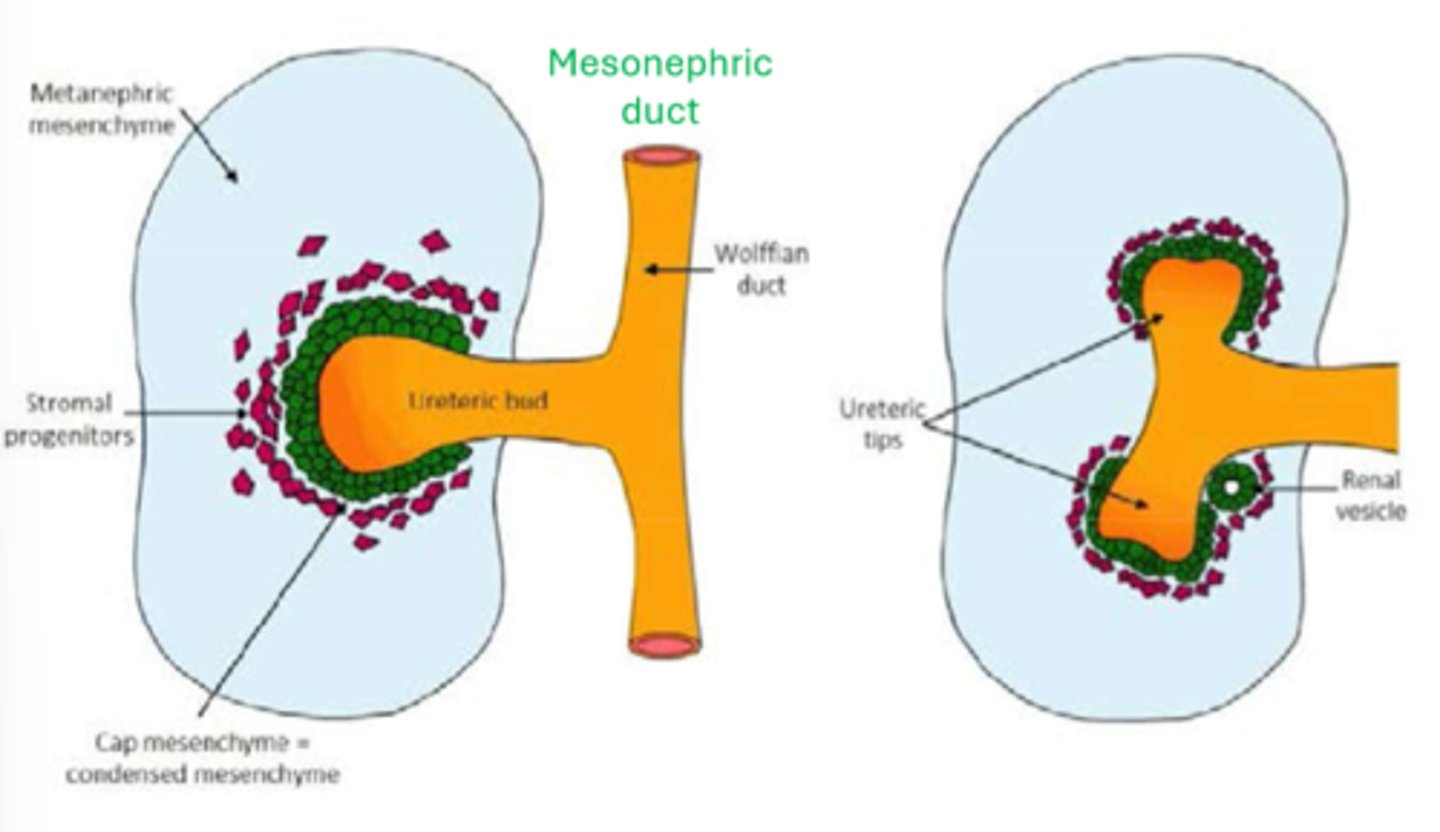
renal vesicles progress through the ___________ shaped body stage and then the ___________ shaped body phase before connecting to the collecting systems of the developing kidney to form nephrons
comma shaped, S shaped
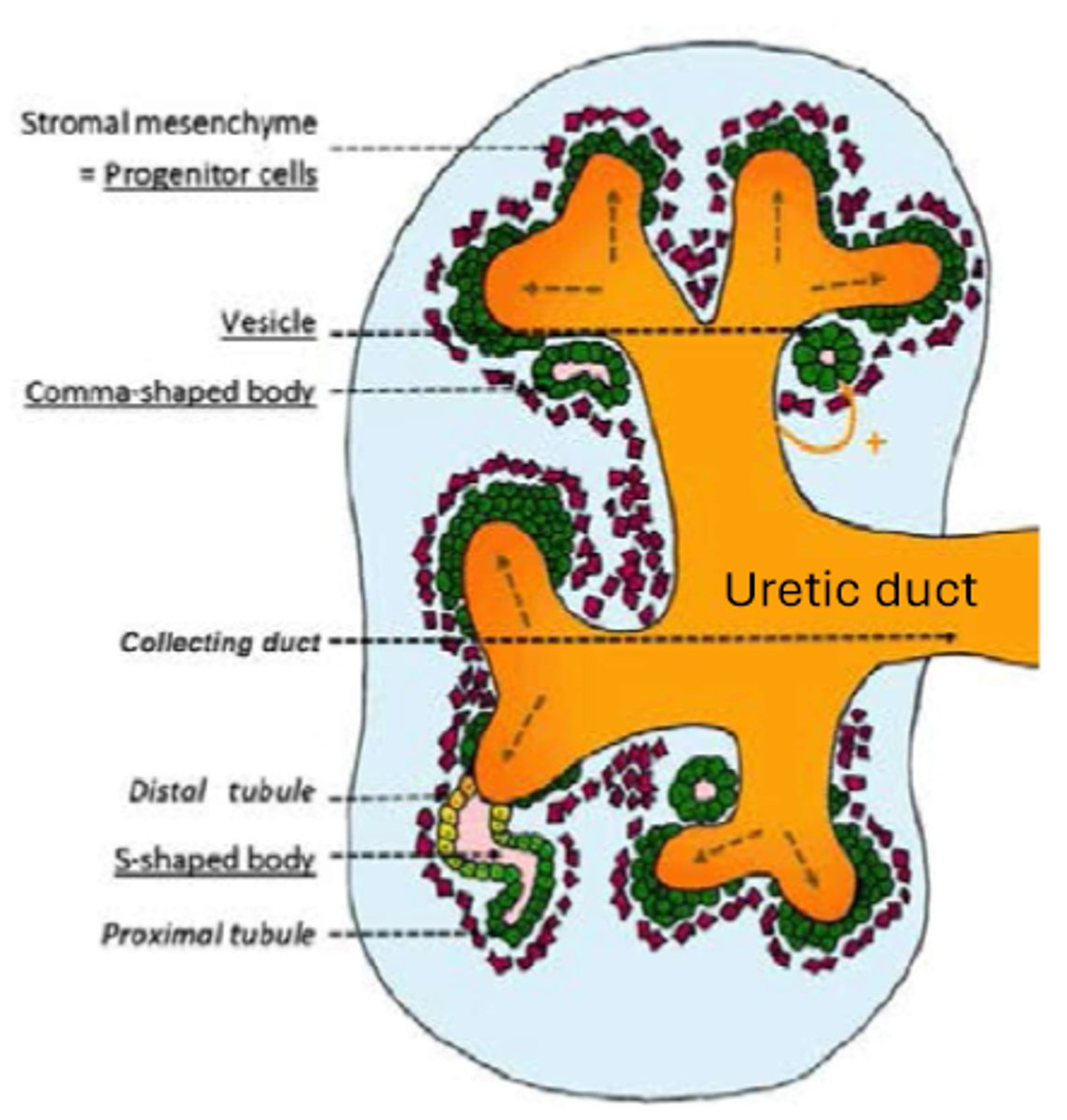
what is the ureteric bud an embryonic precursor for
the renal pelvis
where do the ureter and the male ductus deferens come from in embryonic development
mesonephric/wolffian duct
the ureter originates from a specific outgrowth of the mesonephric duct called the ___________ bud
ureteric
so just to be clear, the ureteric bud comes off of the ___________ duct, and branches into the _______________ mass
mesonephric duct, metanephric mesenchyme/mass
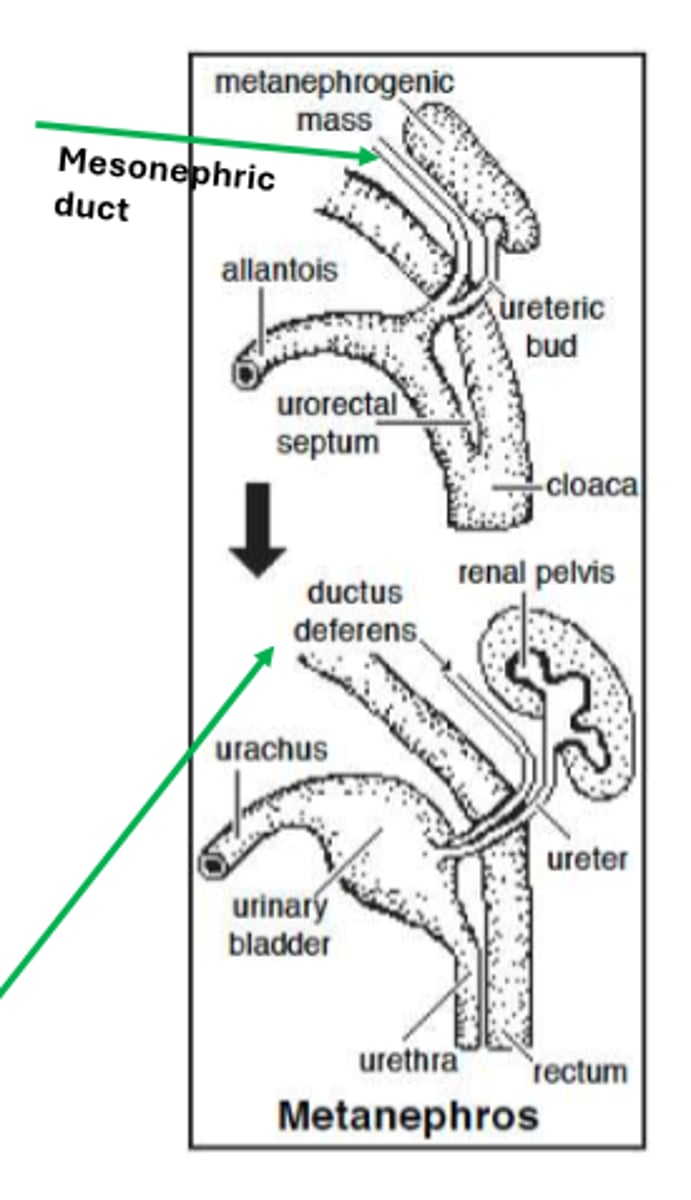
the mesonephric duct serves as the precursor of 3 male urogenital structures
efferent ductules of the testes
epididymis
ductus deferens
mesonephric tubules connected to the rete testis form the 1.) ____________ ______________ of the testis. Cranial part of the mesonephric duct forms the 2.) ________________. Caudal part of the mesonephric duct forms the 3.) ____________ ____________
1. efferent ductules (of the testis)
2. epididymis
3. ductus deferens
the ureteric duct forms the: 5 things
ureter
renal pelvis
major calyces
minor calyces
collecting tubules
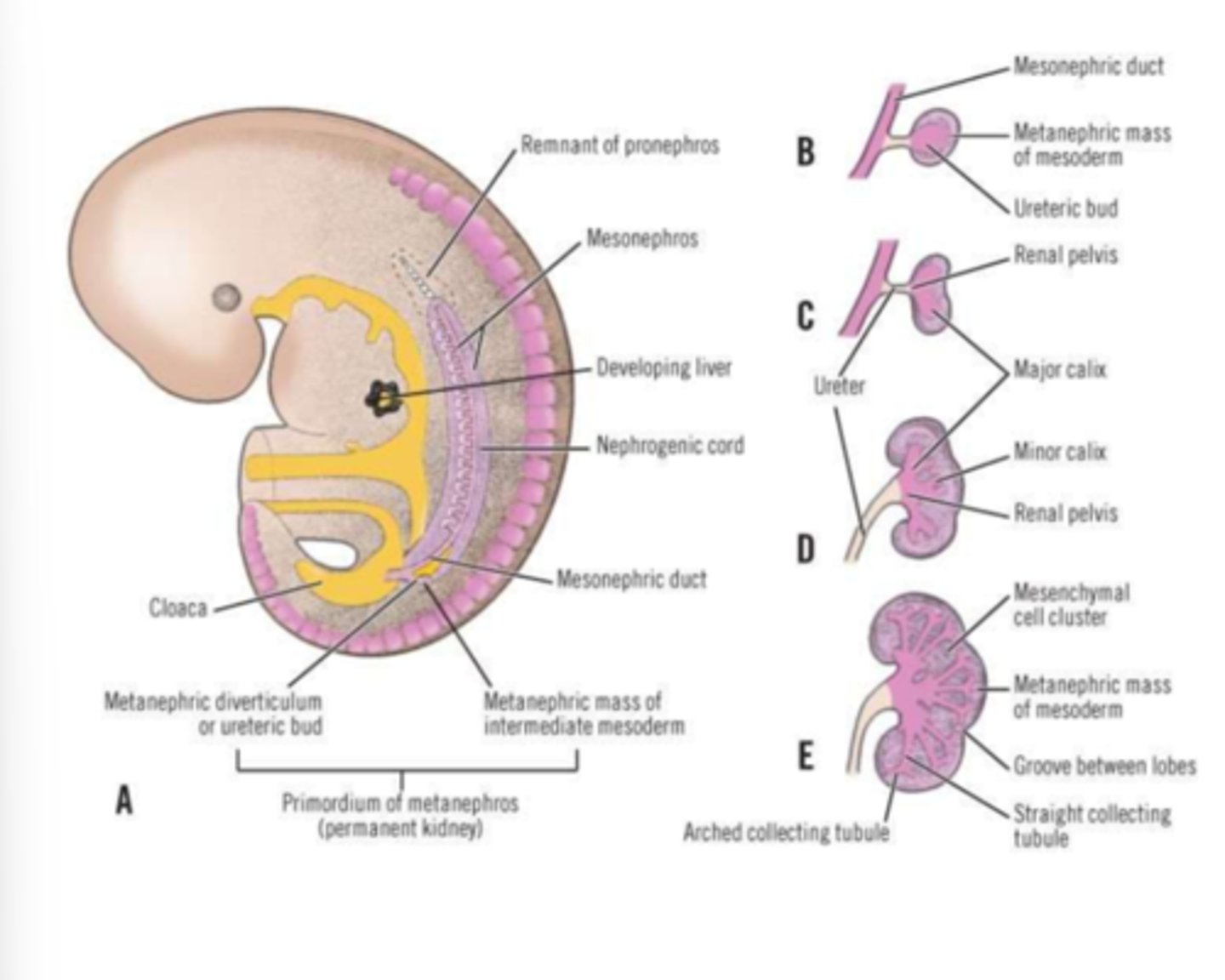
the ureteric bud interacts with the undifferentiated mesoderm called the metanephric mesenchyme to make: 4 things
renal tubules
glomerulus
distal and proximal convoluted tubules
loops of henle
how does the kidney make its way from the tail area to the abdomen region?
starting position - near the embryo's tail, close together in sacral region
ascent - embryo's abdomen straightens, kidneys move apart and ascend to their final position in lumbar region
rotation - kidneys rotate 90 degrees medially around longitudinal axis, resulting in renal pelvis that faces medially
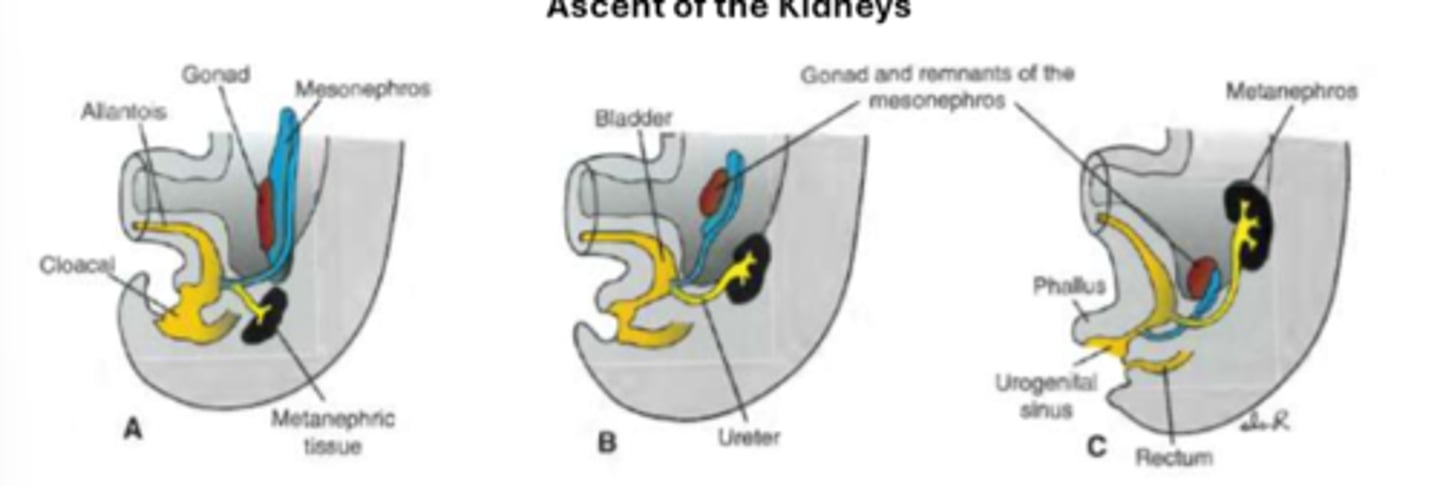
how does the blood supply change as the kidneys ascend
they receive blood from the dorsal aorta through the renal arteries, and as they ascend they receive blood from higher branches of the aorta, as lower branches disintegrate
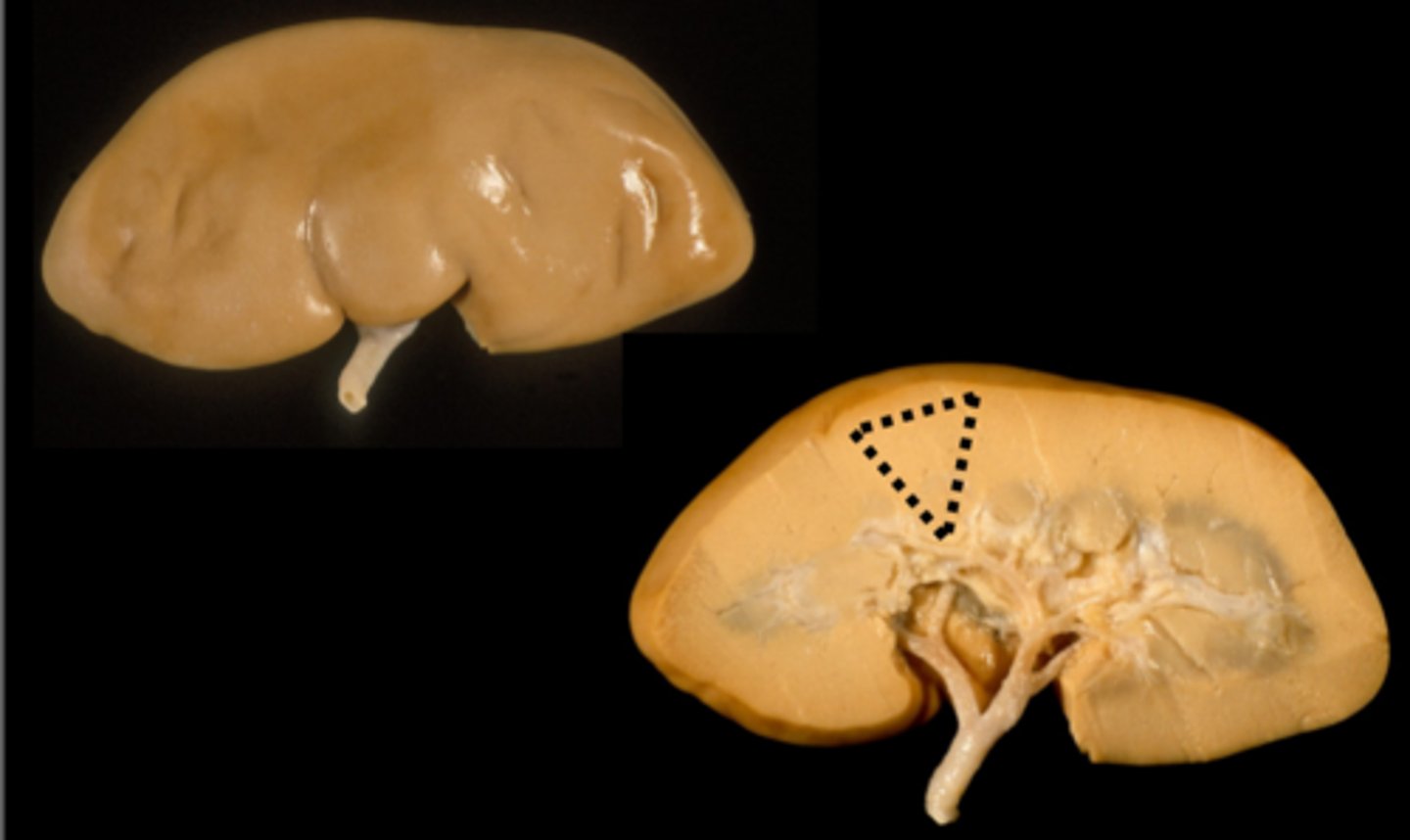
species different kidneys (pic)
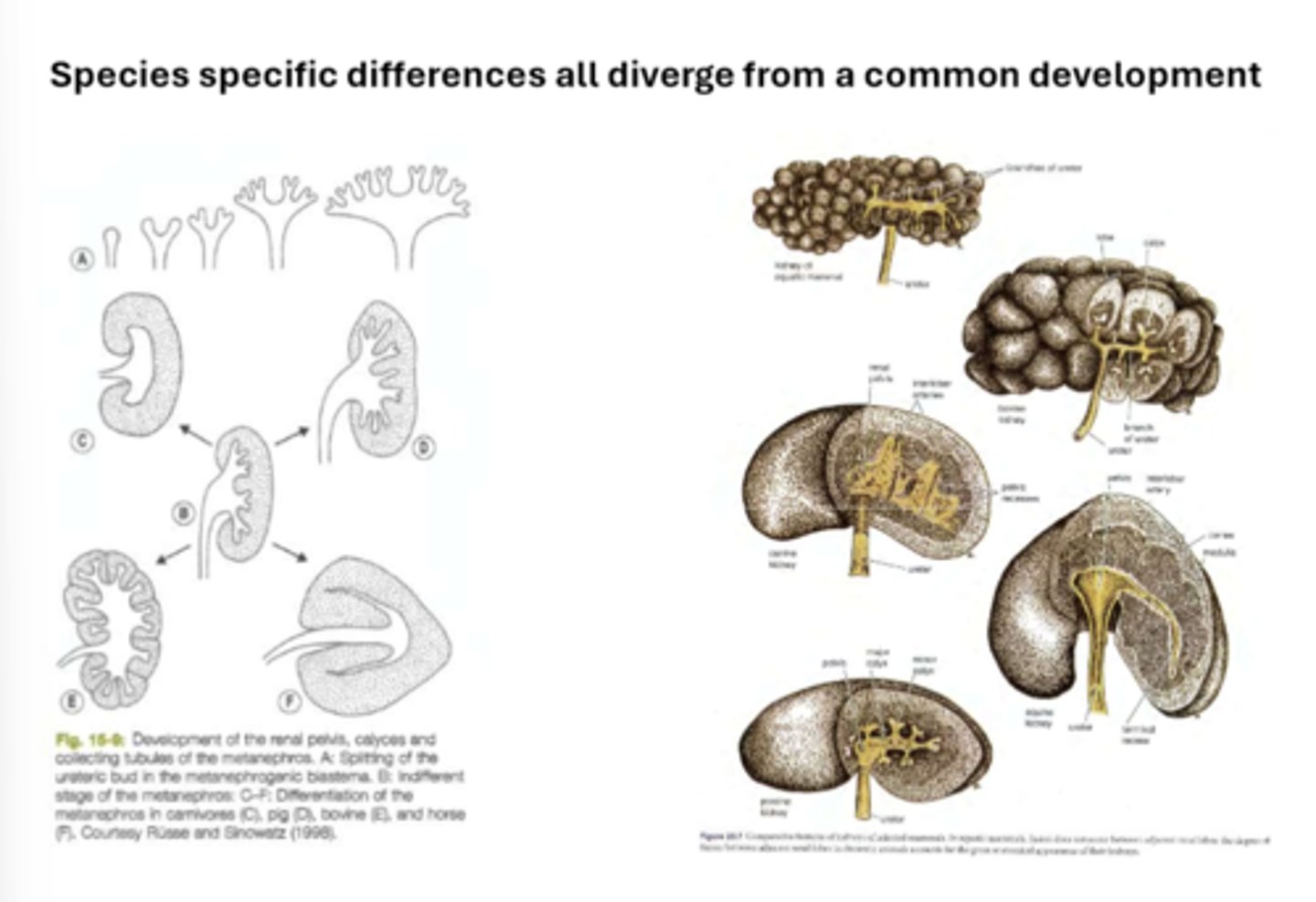
lighter area on outer region of kidney
renal cortex
the (cortex/medulla) contains the renal corpuscles and the proximal and distal convoluted tubules of the nephrons
renal cortex
what is in the renal corpuscles
glomerulus and bowman's capsule
darker area in middle of kidney
renal medulla
the (cortex/medulla) contains the renal pyramids, loops of henle and collecting ducts of the nephrons
renal medulla
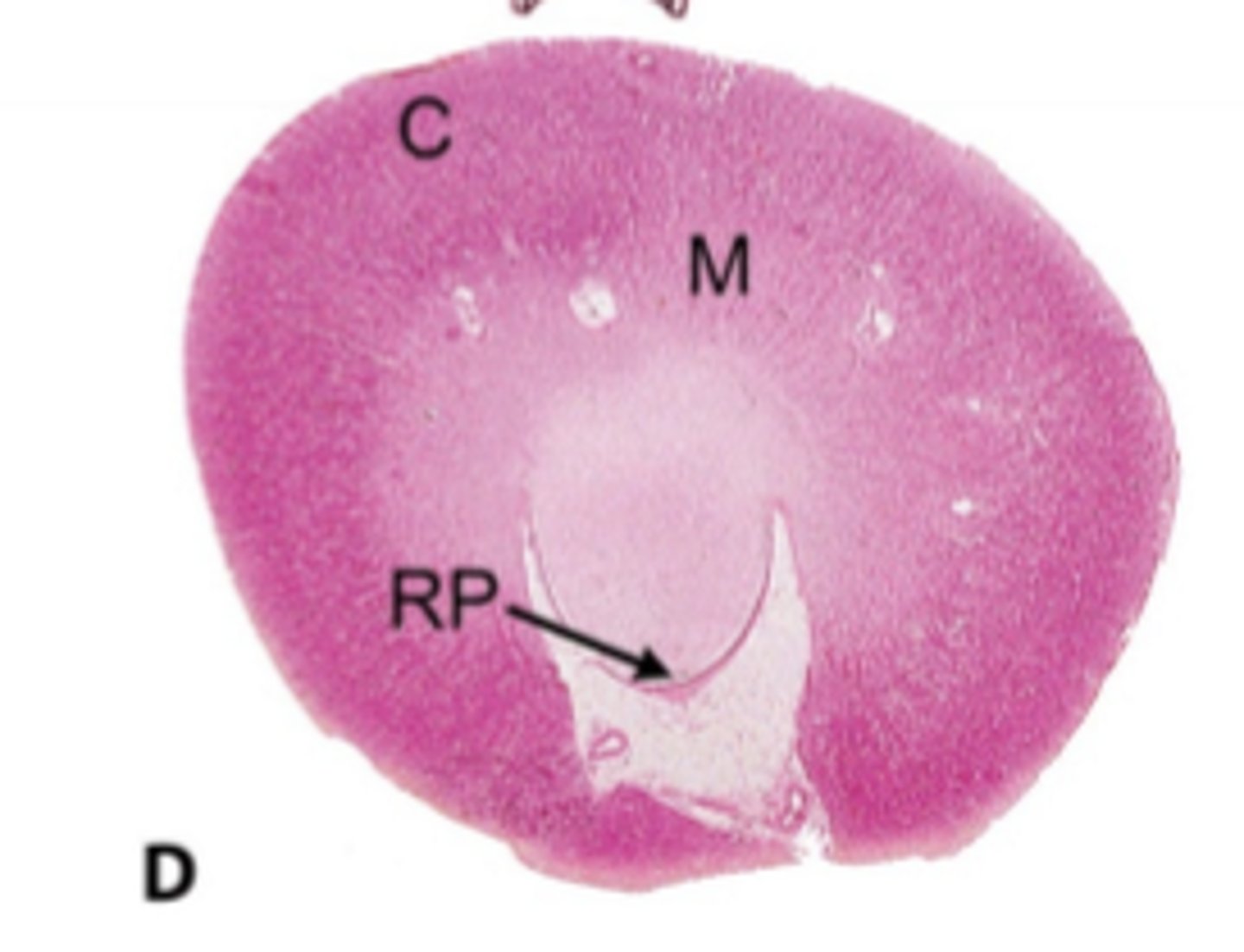
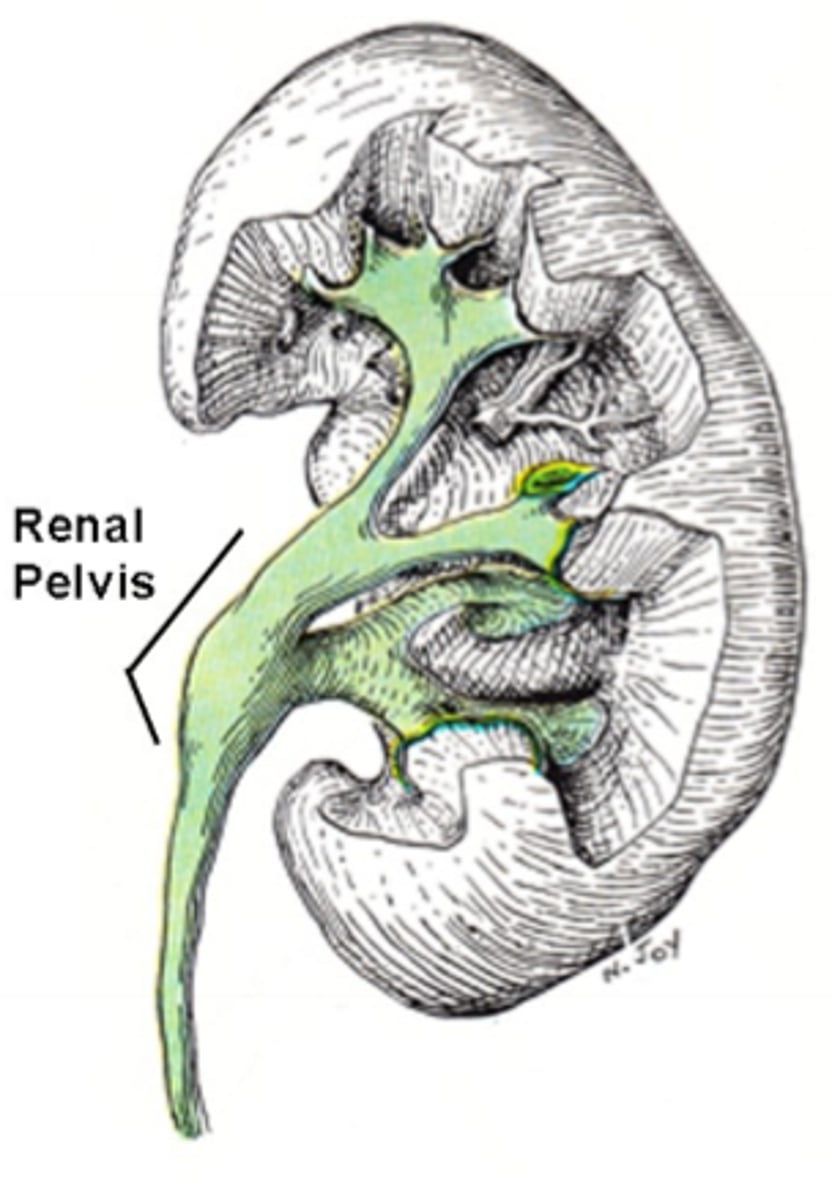
funnel shaped structure in the center of the kidney that collects urine from collecting ducts and channels into ureter
renal pelvis
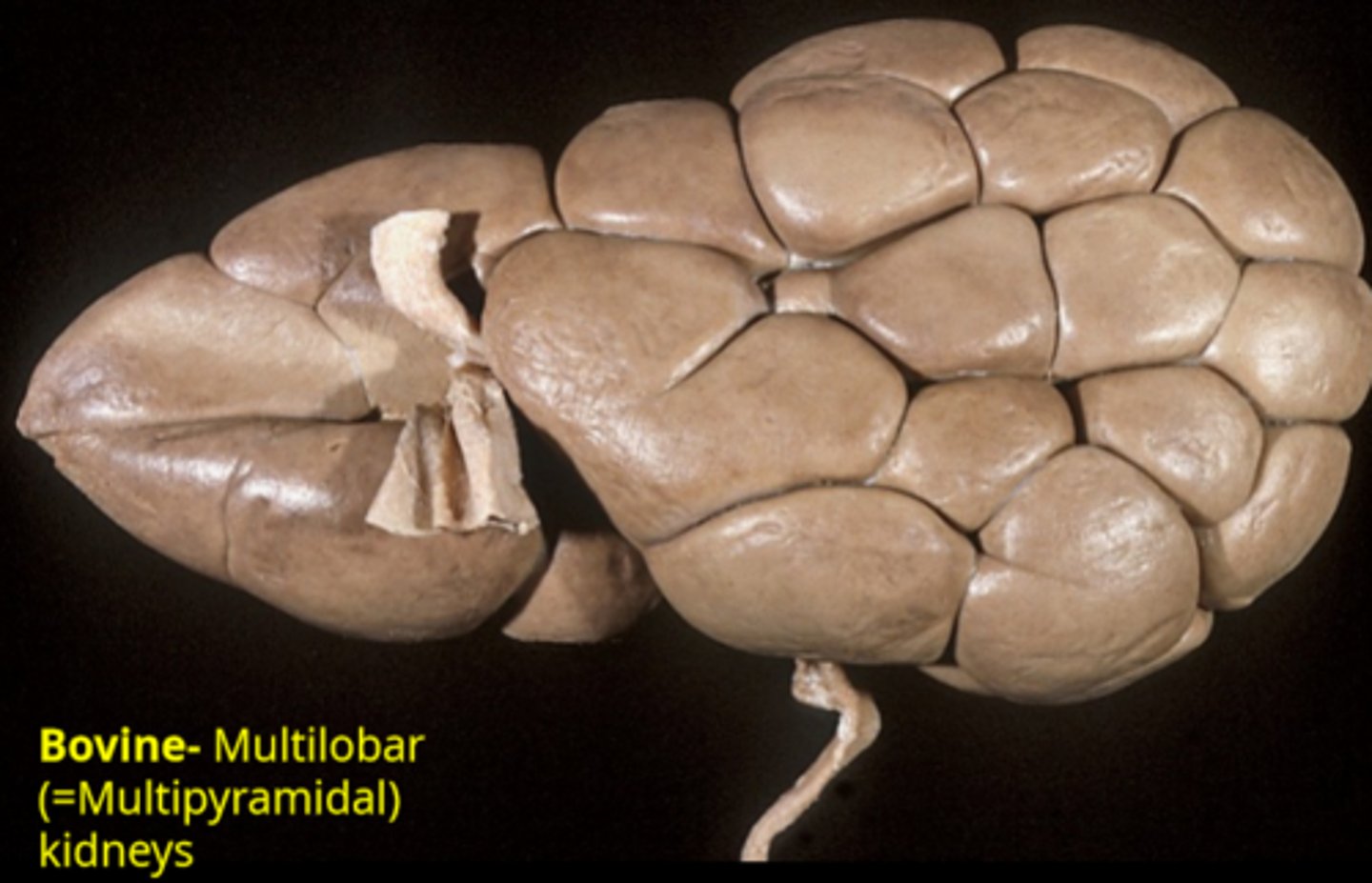
bovine kidney shape
multilobar (multipyramidal)
pig kidney shape
external lobes less present, papillae present
where is the filtrate produced?
renal cortex
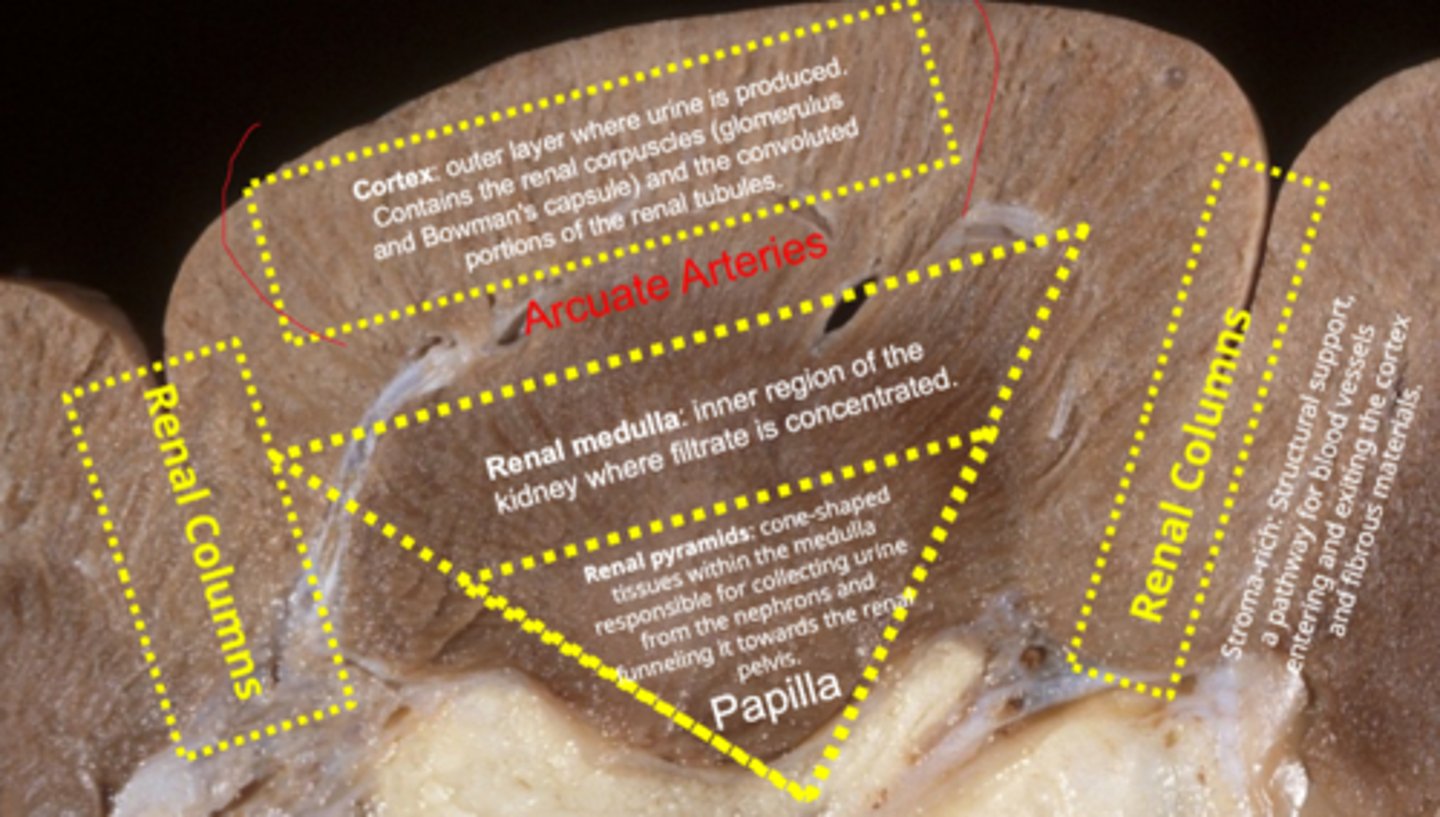
what contains the renal corpuscles (glomerulus and bowman), and the convoluted renal tubules
cortex
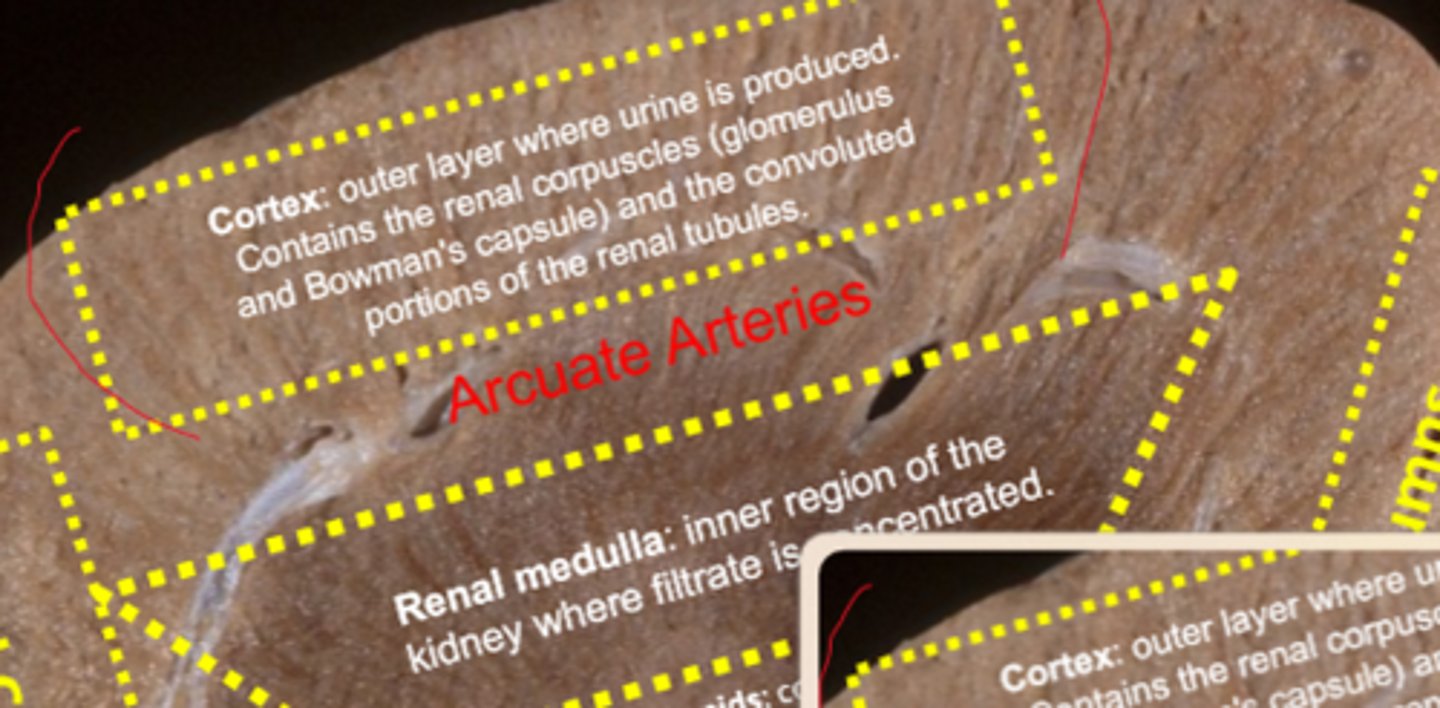
where are the arcuate arteries located
in between the renal cortex and medulla
region of the kidney where filtrate is concentrated
renal medulla
cone-shaped tissues in the medulla for collecting urine from the nephrons and funneling it to the pelvis
renal pyramids
where do you find the straight tubules, loops of henle, and collecting ducts
renal medulla
pathway for blood vessels entering and leaving the cortex, made of fibrous materials
renal columns

shape of canine kidneys
unilobar (unipyramidal) kidneys
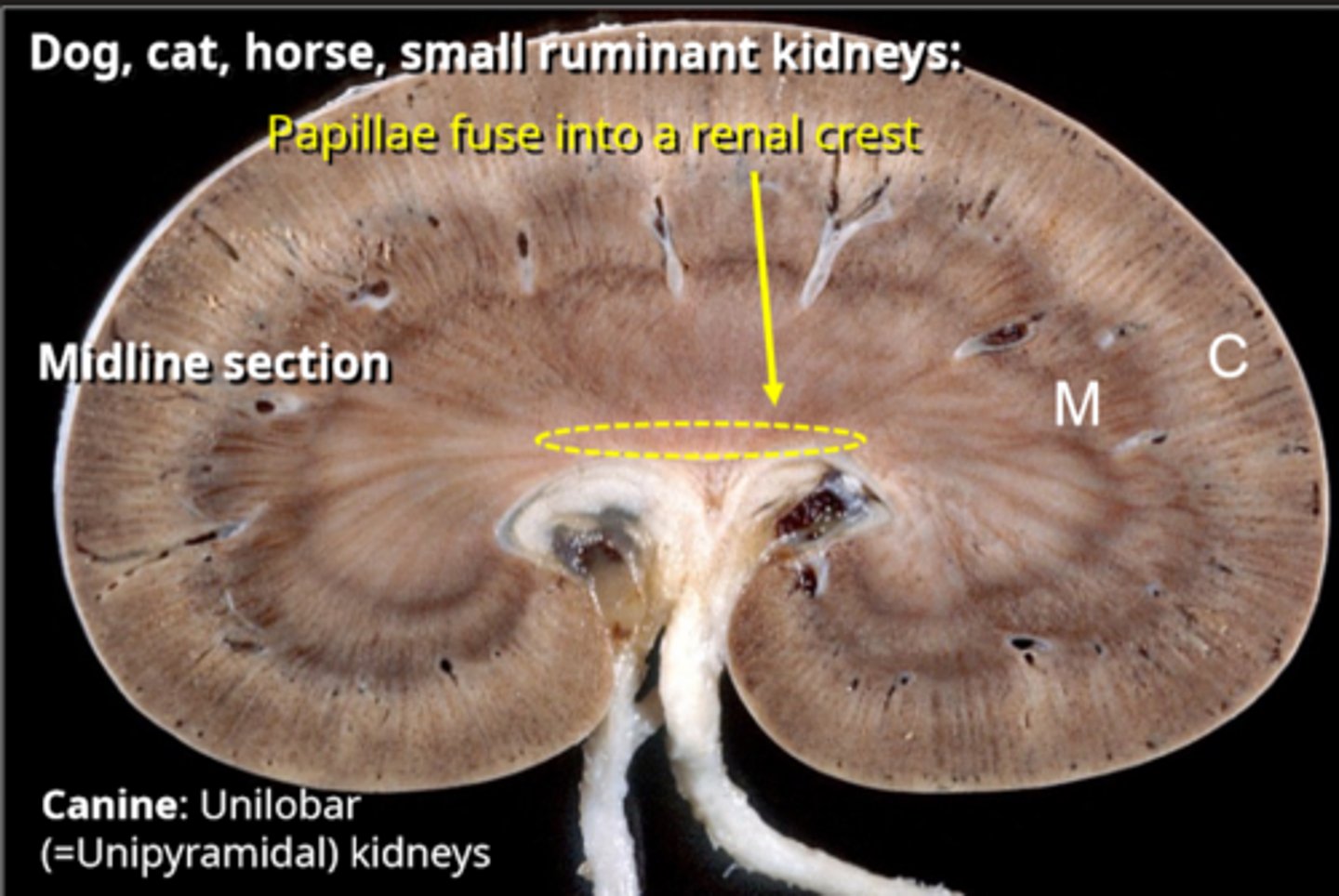
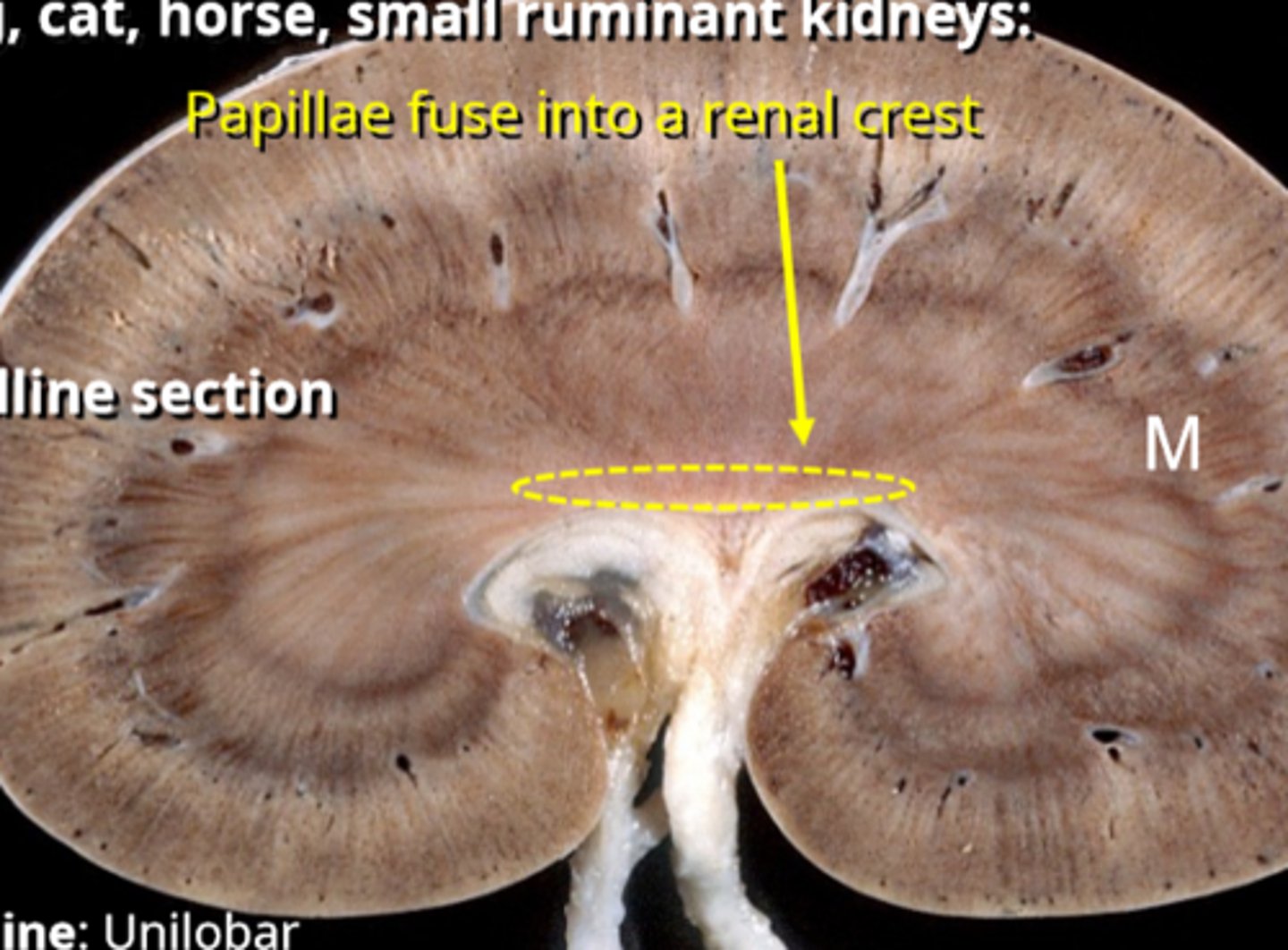
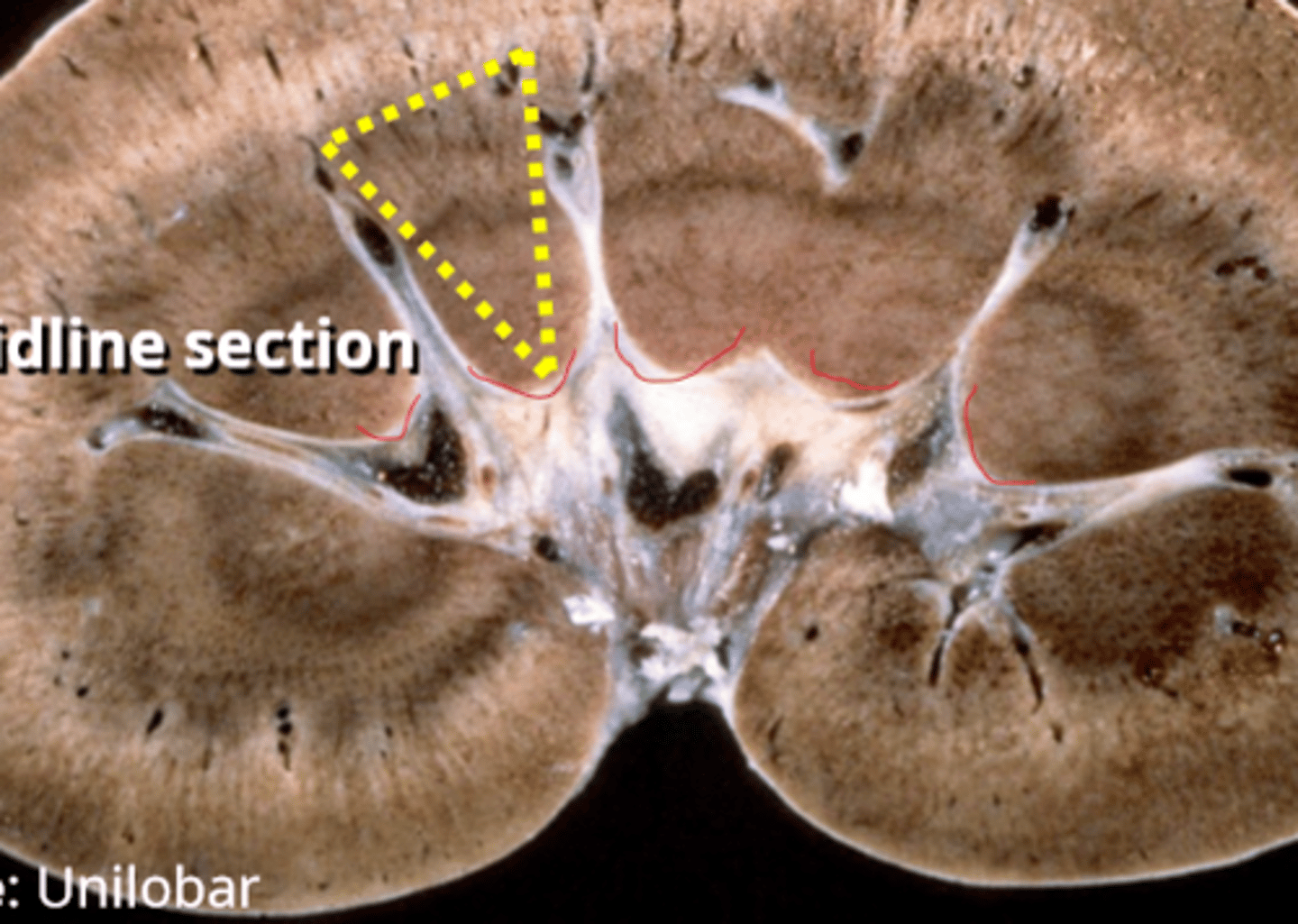
the papillae of each lobe of the kidney fuse into a renal ___________
crest, only seen on a top to bottom cut, not transverse
stroma of the kidney
non-epithelial or endothelial tissue that provides a supportive framework for the renal capsule, glomerulus, vasculature, and interstitium
urine leaves the medulla via the ____________ into the renal pelvis
papillae (lined in red)
what is included in the stroma of the kidney
vasculature, nerves, CT
what is the stroma of the kidney
non-epithelial or endothelial tissue that provides a supportive framework
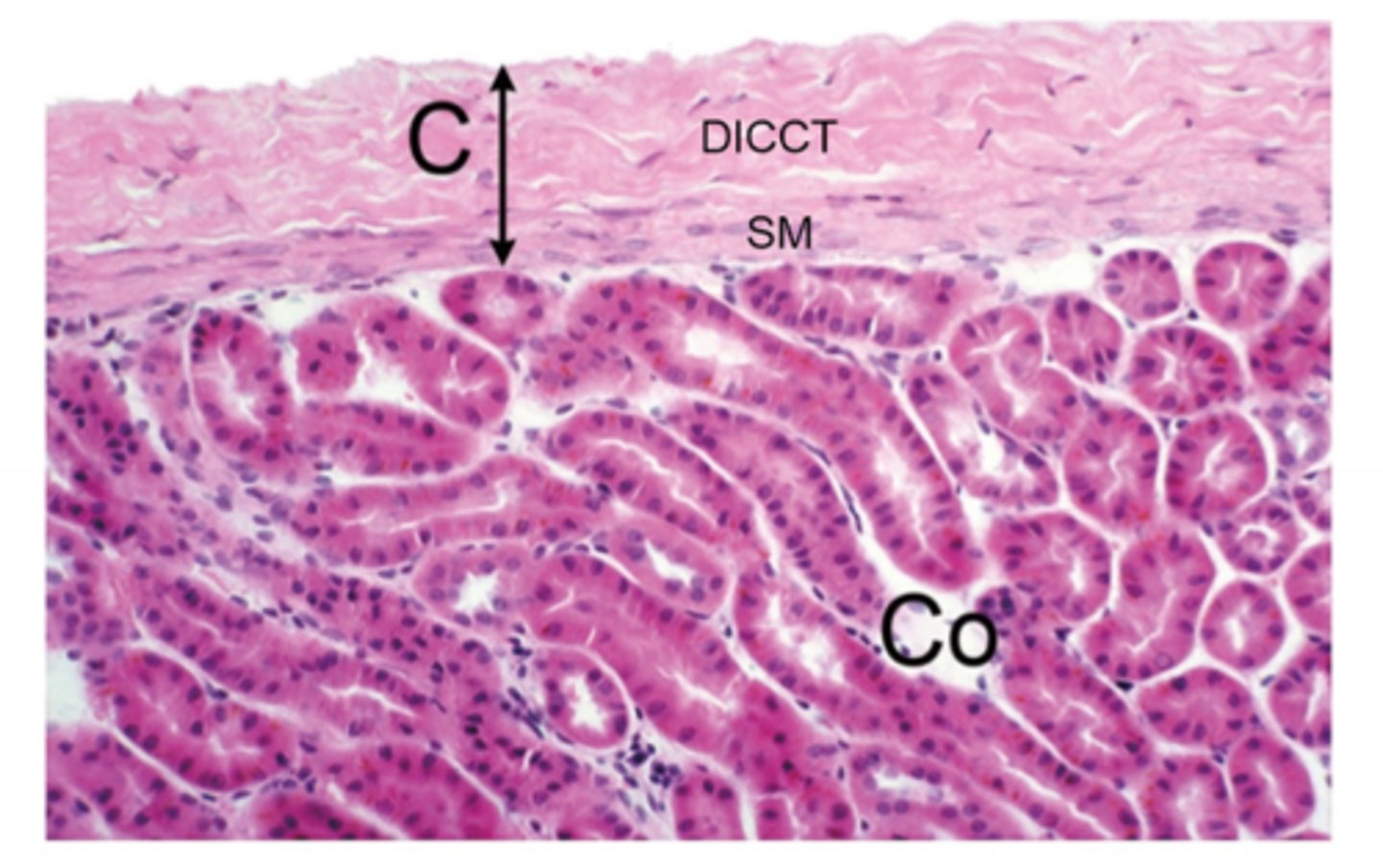
outer layer of the renal capsule
DICCT
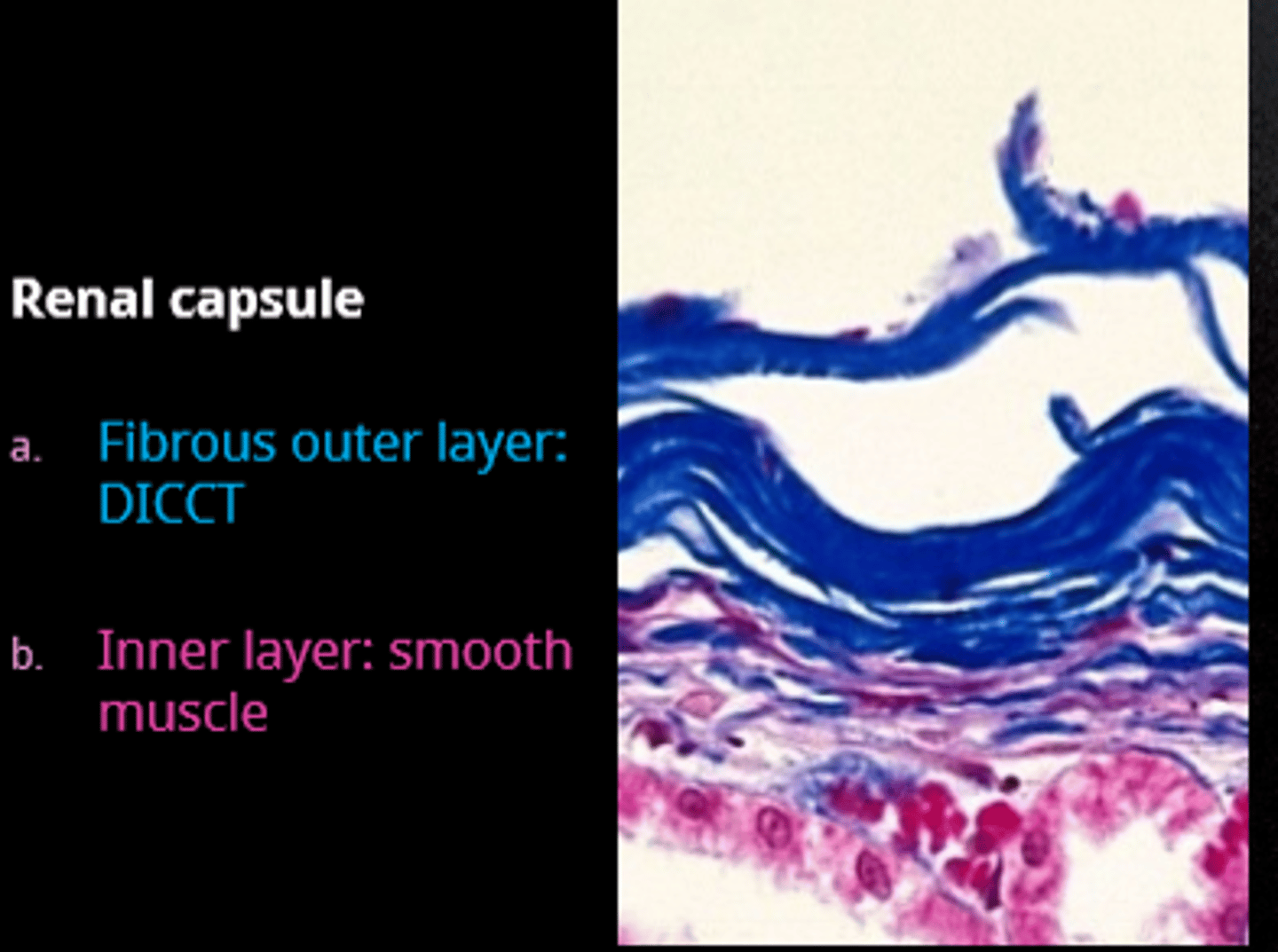
inner layer of the renal capsule
smooth muscle
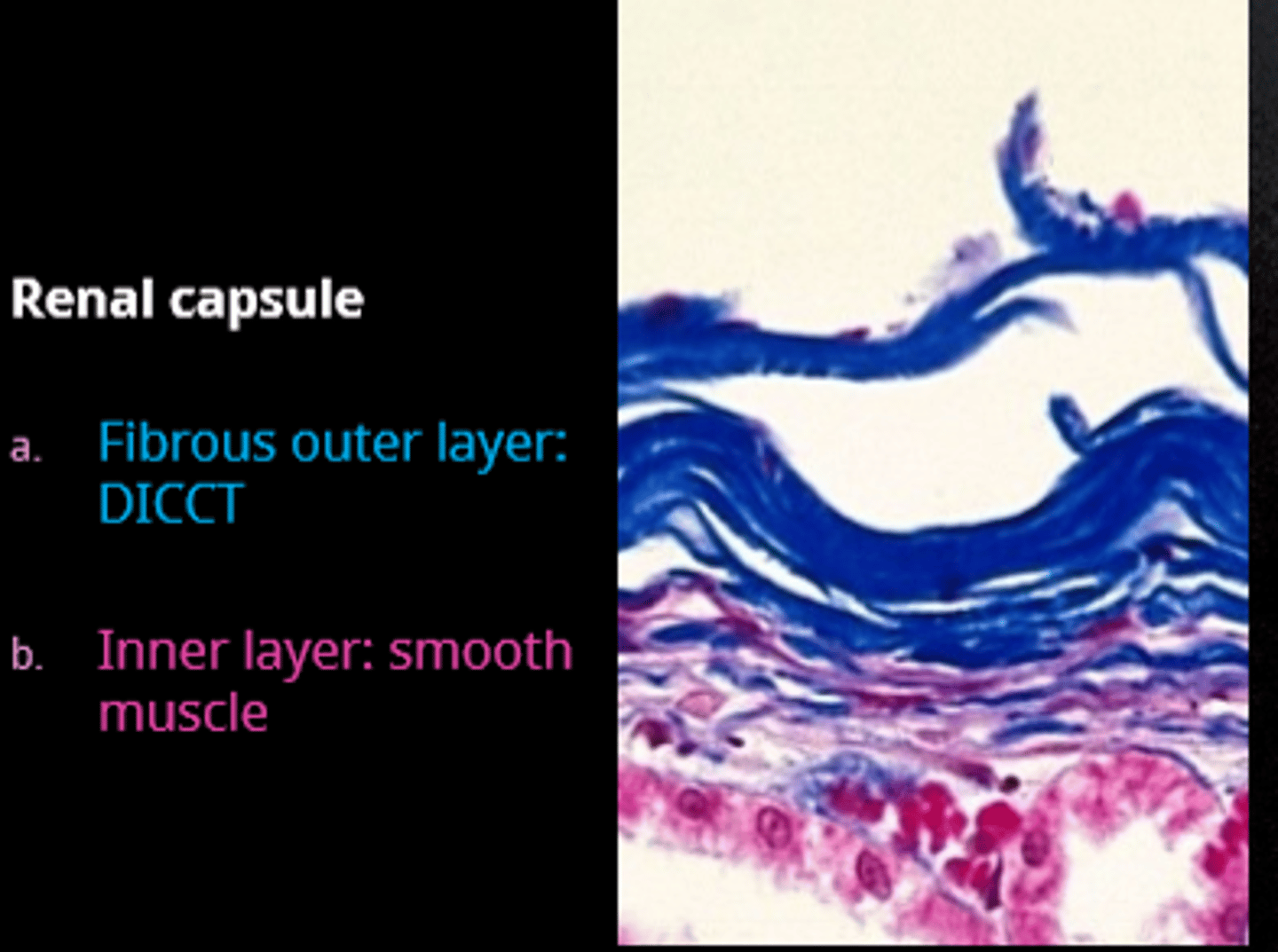
Capsule and cortex
what makes up the parenchyma of the kidney
uriniferous/renal tubules
two parts of the uriniferous tubules
nephrons and collecting ducts (both come from intermediate mesoderm)
what do the nephrons derive from
metanephric mesenchyme
what do the collecting ducts derive from
uretic duct
6 segments of the nephron (in order)
glomerular capsule
proximal convoluted tubule
proximal straight tubule/descending thick loop
thin tubule
distal straight tubule/ascending thick loop
distal convoluted tubule
the glomerulus serves as a __________
filter for big stuff like proteins
what does the glomerulus filter out
large stuff, like blood and proteins
where is salt pumped out of the nephron
ascending limb
how is water removed from the filtrate
mainly as the salty medulla pulls the water out of the descending limb/collecting duct using osmosis
what happens in the proximal tubule
things the body wants, such as glucose, are removed here
path through the nephron 7
proximal convoluted tubule
descending thick limb of Henle's loop
descending thin limb
thick ascending limb
distal convoluted tubule
collecting duct

what happens in the proximal convoluted tubule
filtrate is reabsorbed along with glucose, amino acids, small proteins, and most NaCl and H20
the tubular fluid in the proximal convoluted tubule is ___________
isotonic, pretty much the same concentration-wise as the intercellular fluid
structure of nephron in proximal convoluted tubule
super mitochondrial rich - little streaky bits
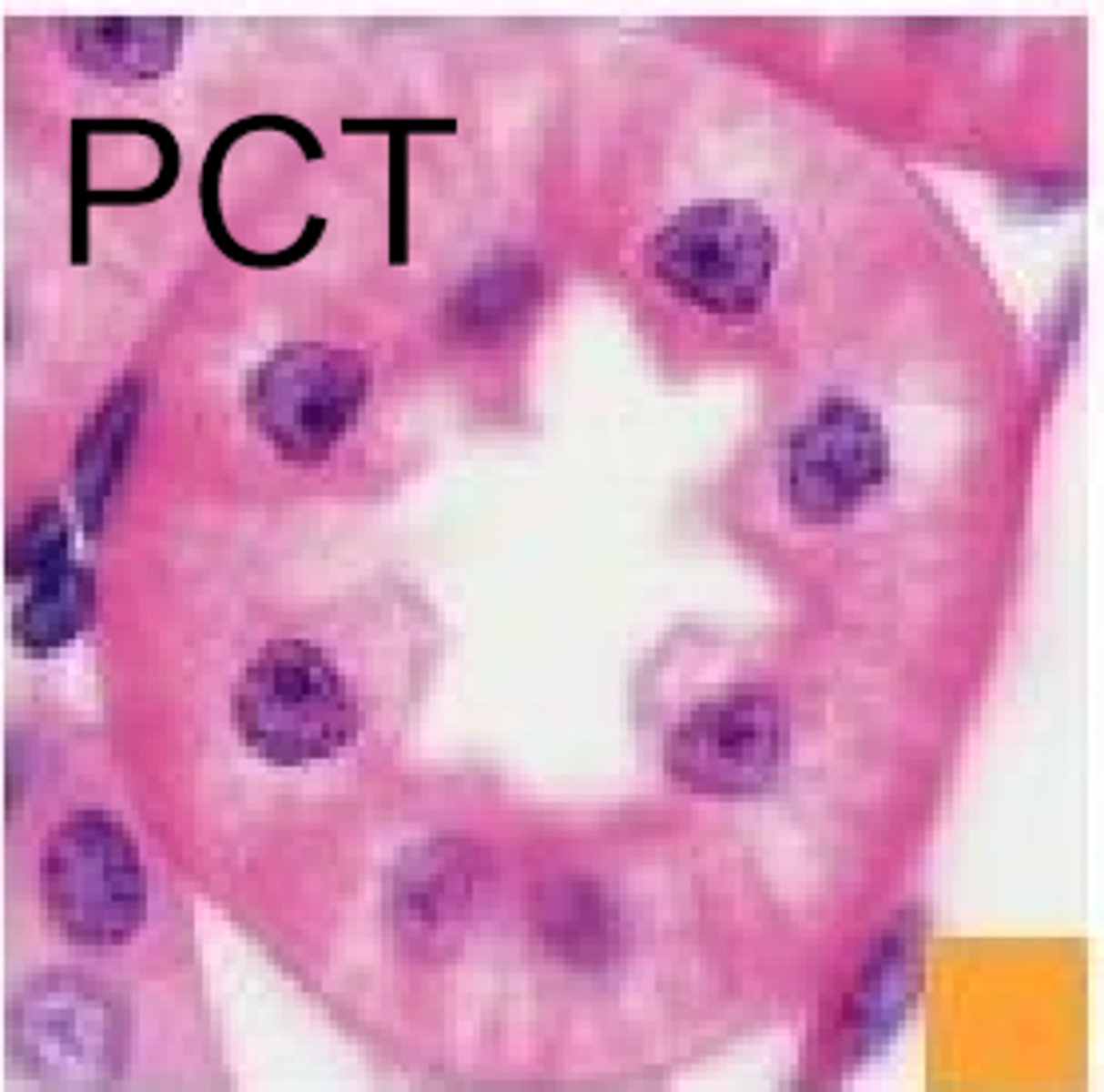
what happens in the proximal straight tubule
water is reabsorbed, NaCl is not
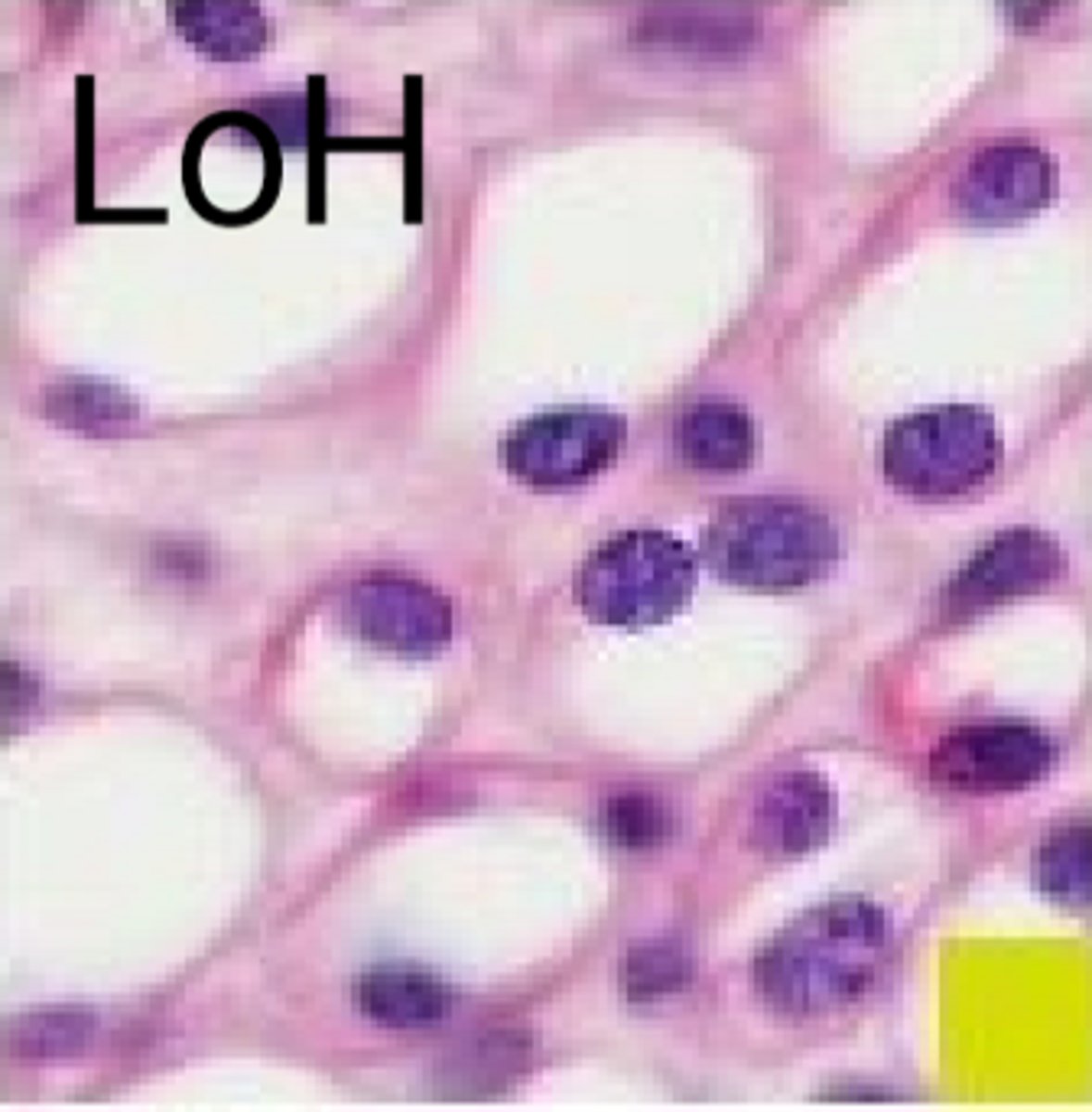
what happens in the descending thin limb
water leaves the tubule to equilibrate with the salty interstitium
structure of nephron in loop of henle
thin tubules don't require ATP, water is just trying to diffuse out
-don't require mitochondrias as much
-squamous endothelium
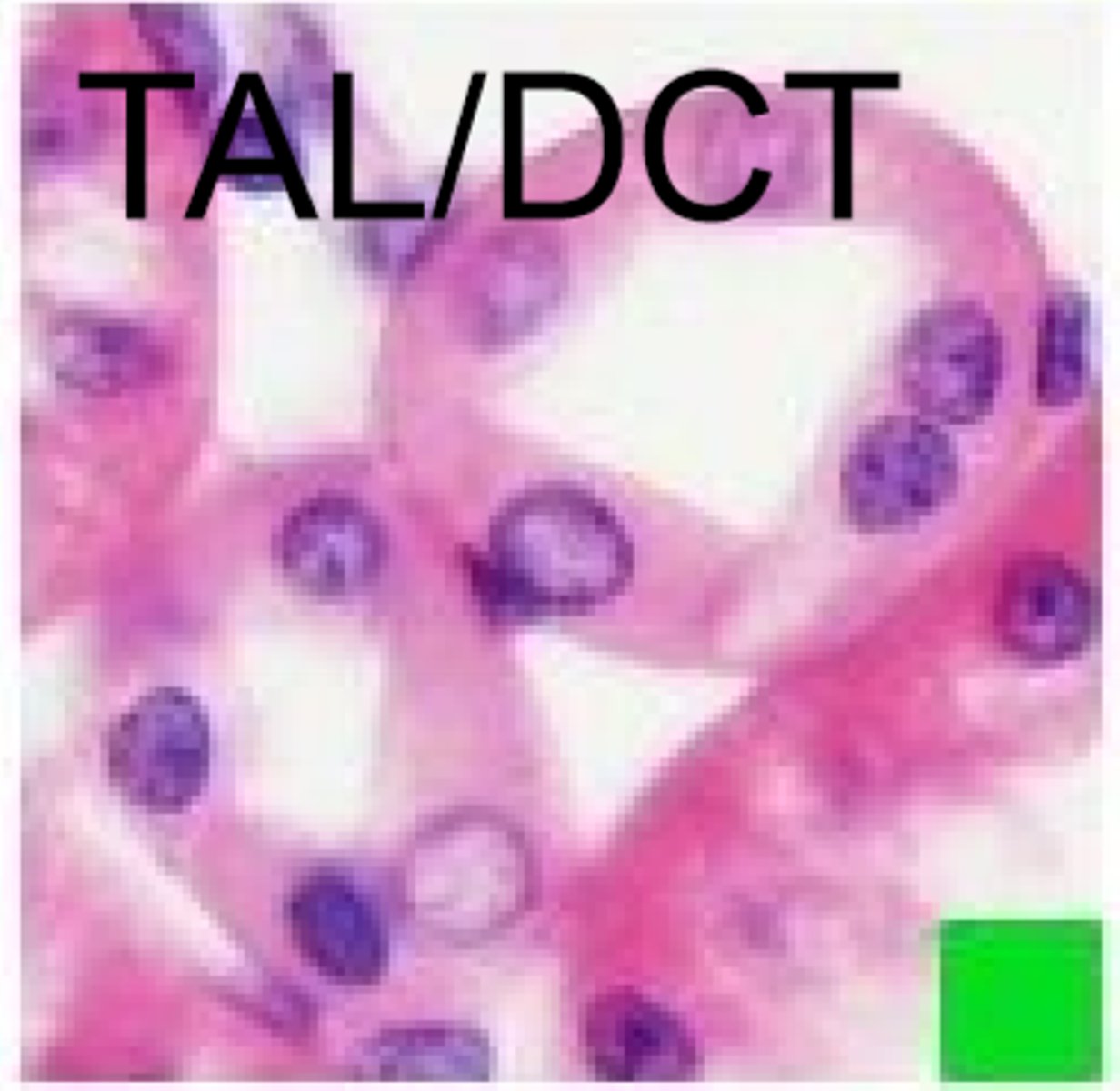
what happens in the thick ascending limb
forms the macula densa, acts as a Na+ sensor
structure of nephron in thick ascending limb
more cuboidal, no brush border
what happens in the collecting tubule/duct
urine composition is regulated, acid/base regulation, Na+, K+ and water regulated
structure of nephron in collecting duct
hormone (ADH) activity, acid-base balance requires thicker cells again
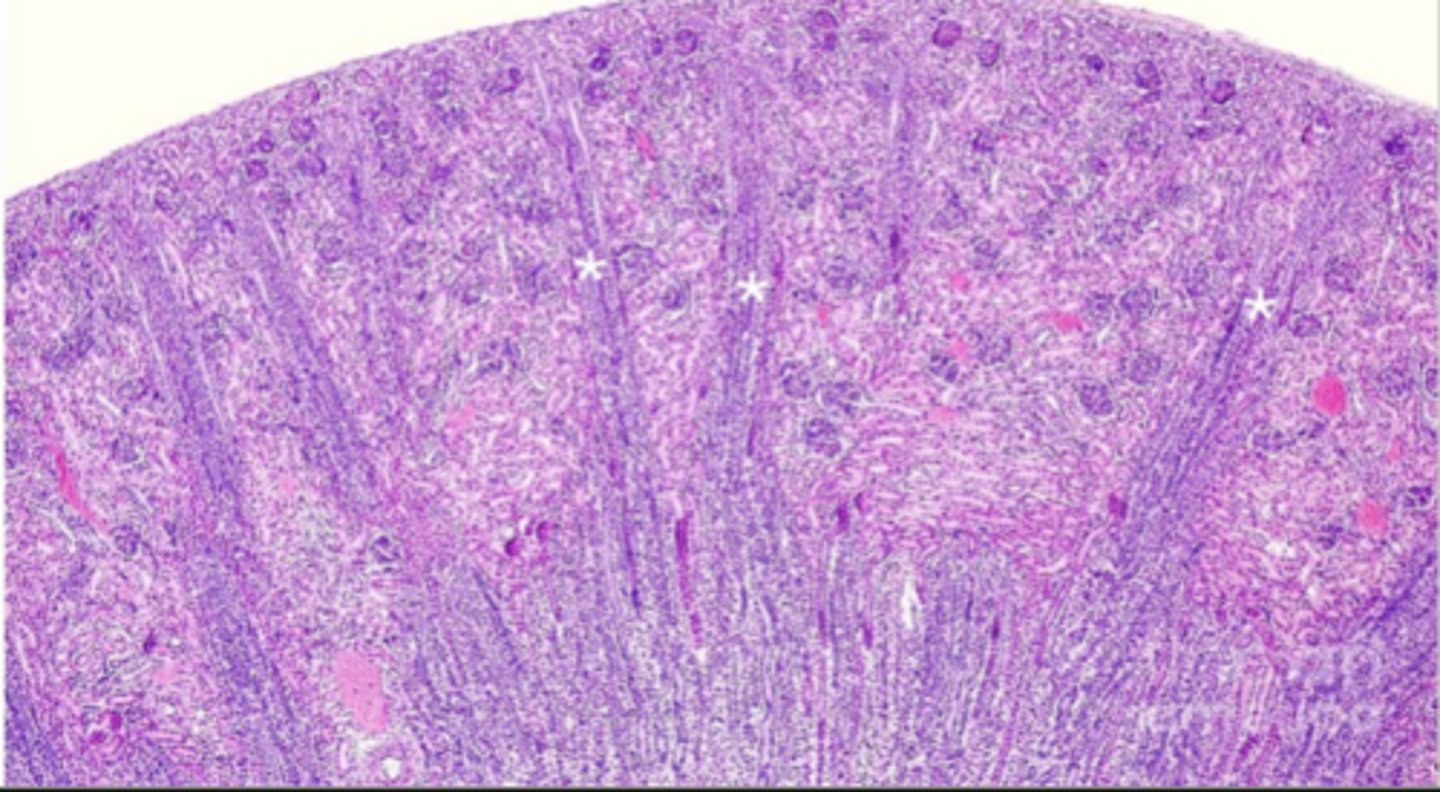
two types of structure in the cortex
medullary rays
cortical labyrinth
what is in the medullary rays
straight tubules and collecting ducts (green boxes)
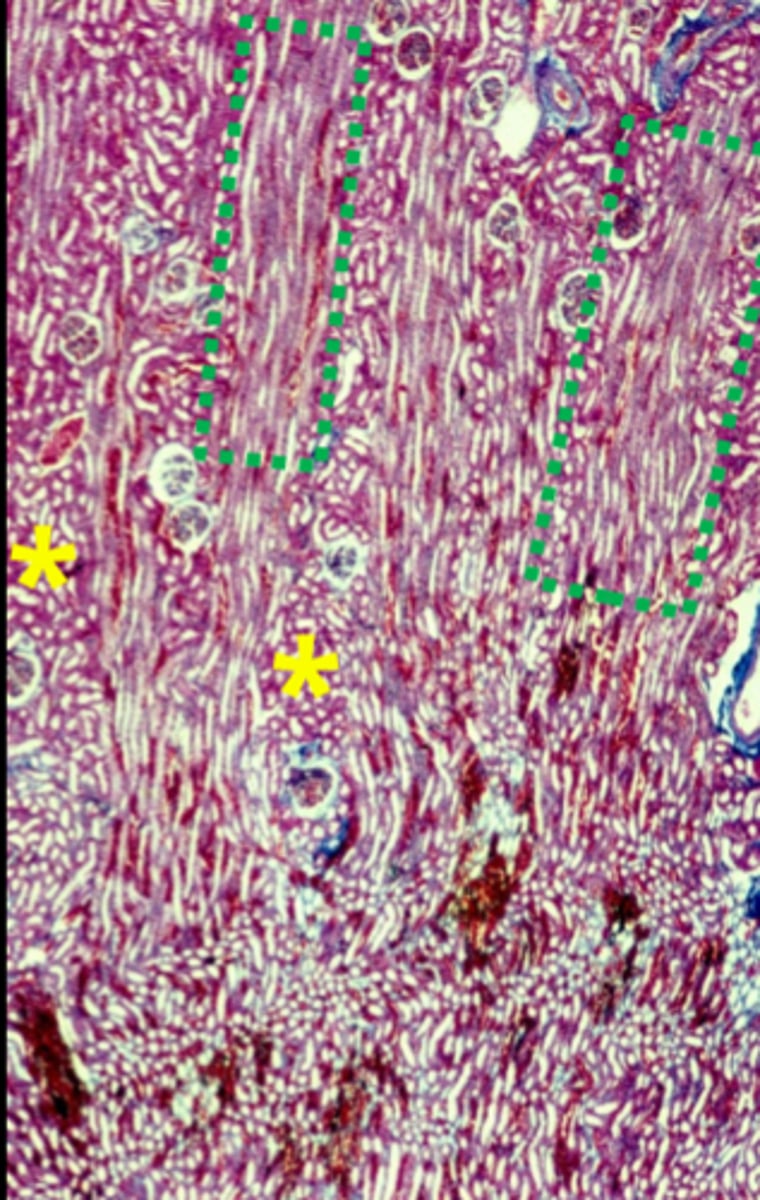
what is in the cortical labyrinth
convoluted tubules, and glomeruli
what is in the cortical labyrinth 4
renal corpuscles,
irregular sections of the PCT,DCT
distal thick ascending limb
initial collecting tubule portion

what is in the medullary rays 2
proximal and distal straight tubules
arched collecting tubules and straight collecting tubules
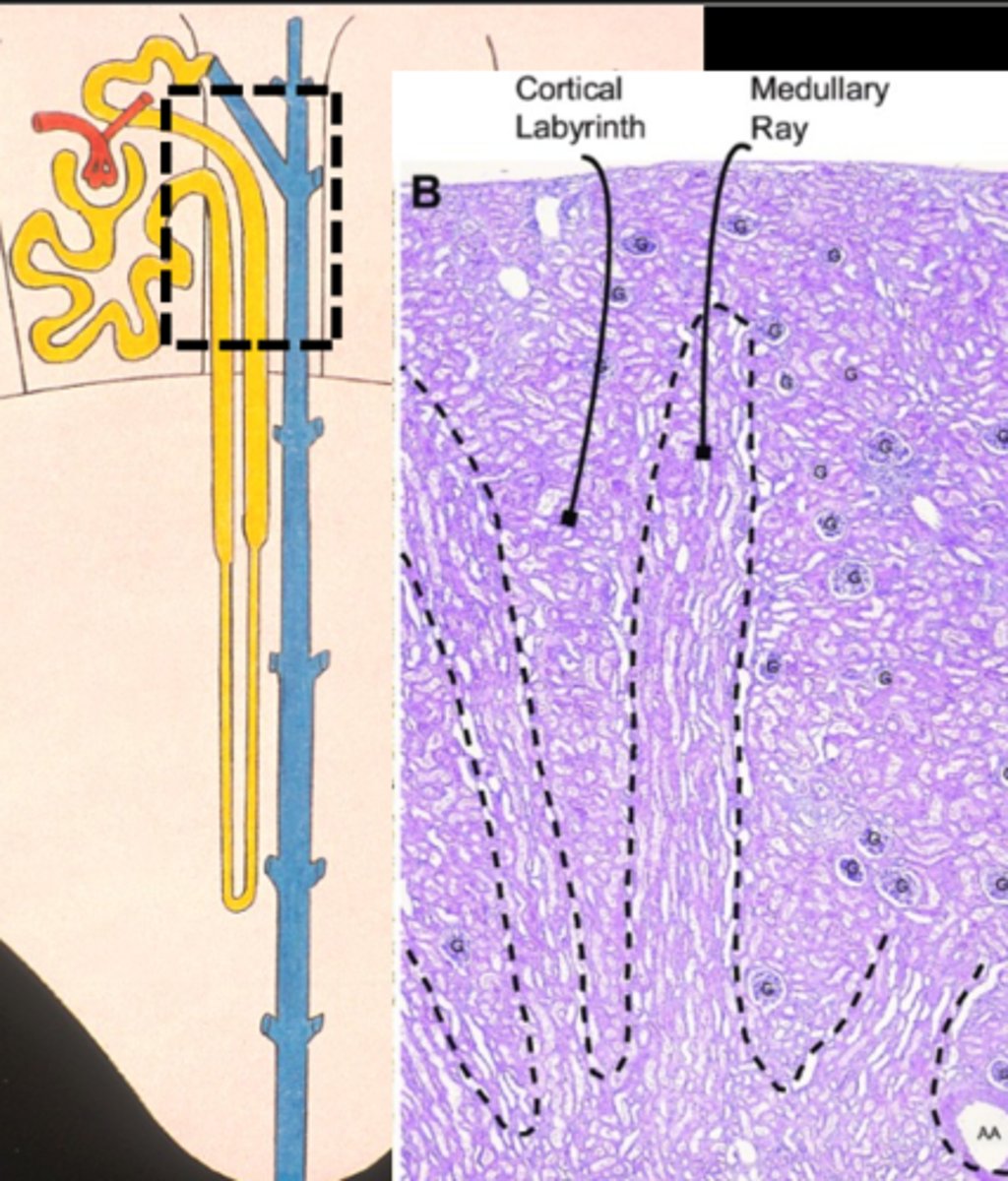
the medullary rays are only in the ___________ of the kidney
cortex
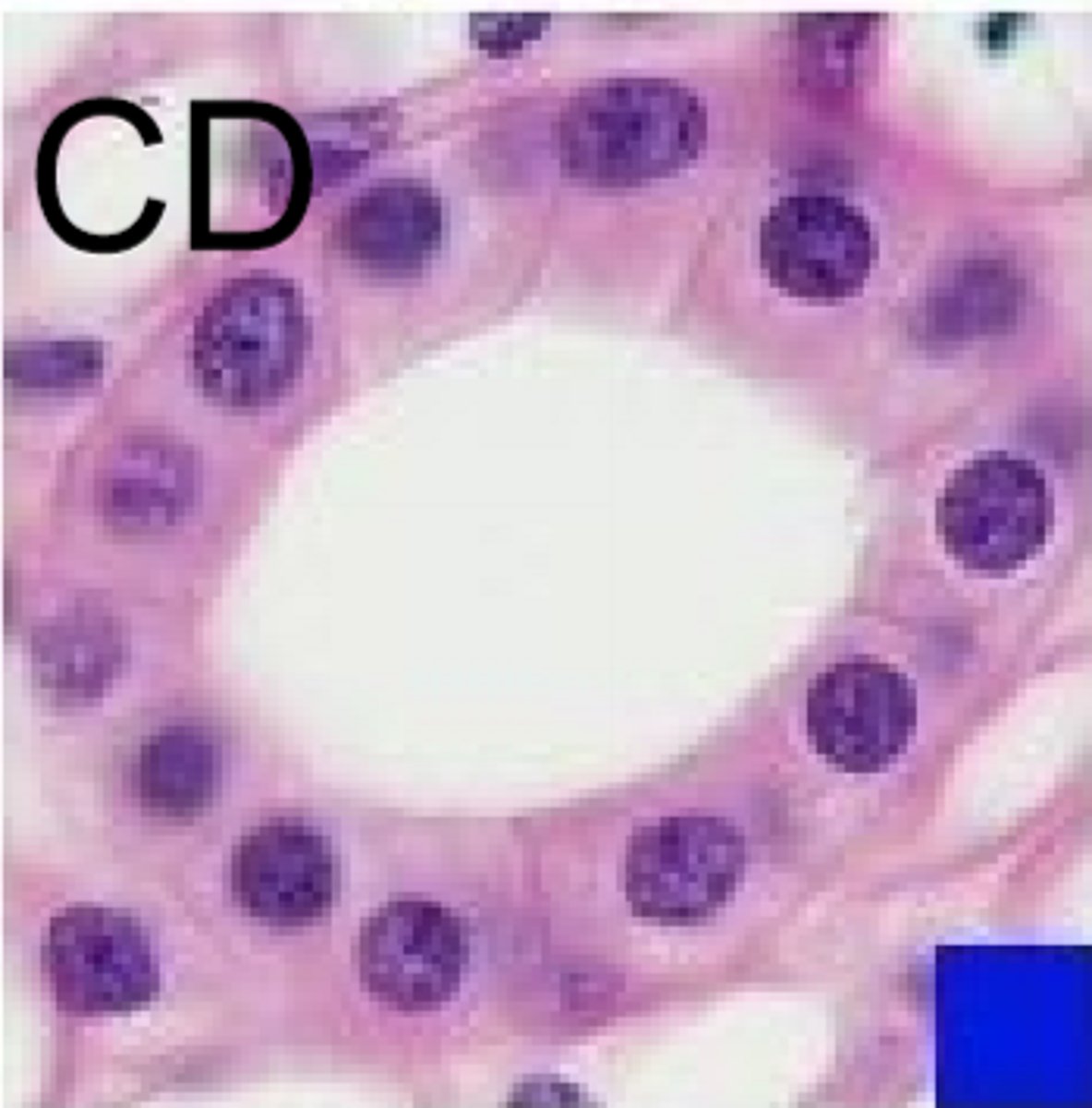
what is inside the renal corpuscle
glomerulus and bowman's capsule
- capillary bed between an afferent and efferent arteriole
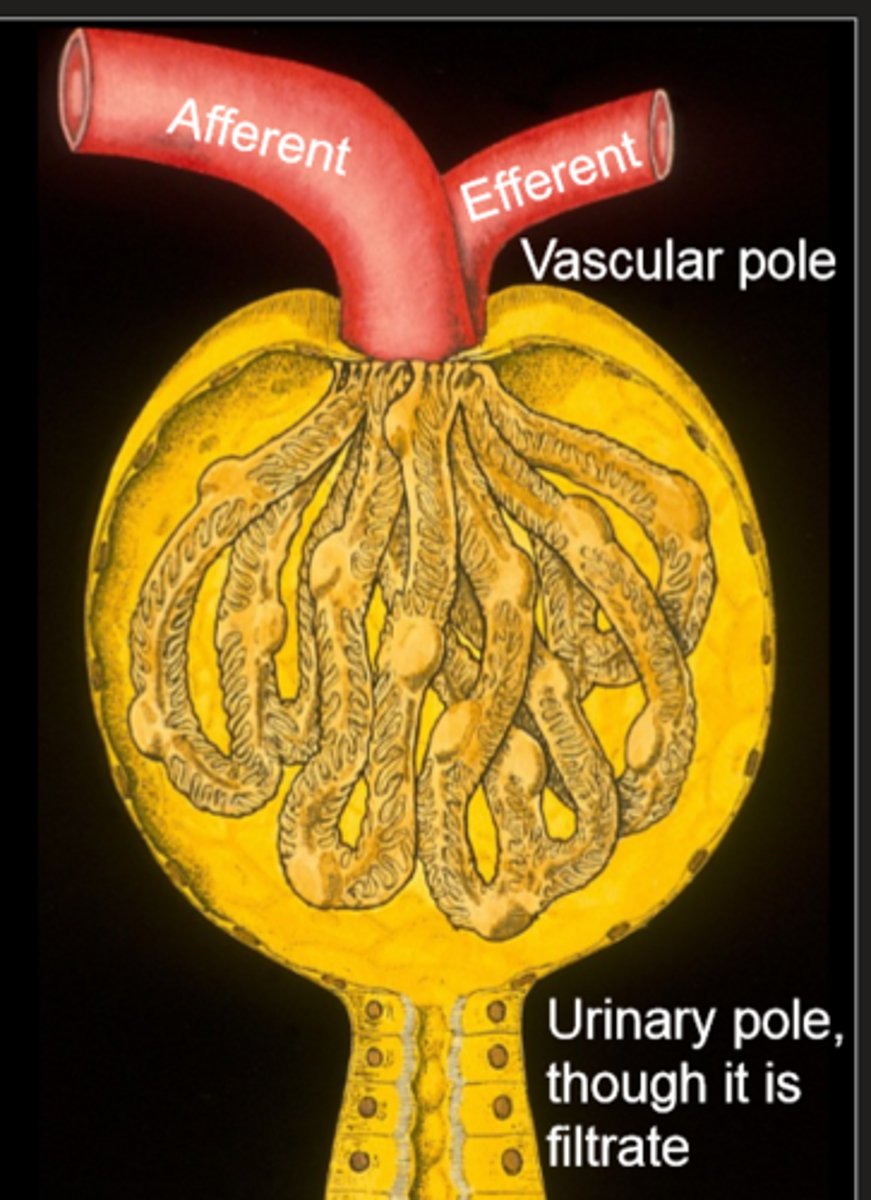
place where the afferent and efferent arterioles connect to the renal corpuscle
vascular pole